Role of the high-affinity zinc uptake znuABC system in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium virulence
- PMID: 12117991
- PMCID: PMC128140
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4721-4725.2002
Role of the high-affinity zinc uptake znuABC system in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium virulence
Abstract
The Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium znuABC genes encoding a high-affinity zinc uptake system and its regulatory zur gene have been cloned. Salmonella serovar Typhimurium zur and znuC knockout mutants have been constructed by marker exchange. The 50% lethal dose of the znuC mutant increased when either orally or intraperitoneally inoculated in BALB/c mice, while virulence of the zur mutant decreased only when mice were intraperitoneally challenged.
Figures
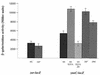
References
-
- Althaus, E. W., C. E. Outten, K. E. Olson, H. Cao, and T. V. O'Halloran. 1999. The ferric uptake regulation (Fur) repressor is a zinc metalloprotein. Biochemistry 38:6559-6569. - PubMed
-
- Beard, S. J., R. Hashim, G. Wu, M. R. B. Binet, M. N. Hughes, and R. K. Poole. 2000. Evidence for the transport of zinc(II) ions via the Pit inorganic phosphate transport system in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 184:231-235. - PubMed
-
- Dalet, K., E. Gouin, Y. Cenatiempo, P. Cossart, and Y. Hechard. 1999. Characterisation of a new operon encoding a Zur-like protein and an associated ABC zinc permease in Listeria monocytogenes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 174:111-116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

