Mossy fiber Zn2+ spillover modulates heterosynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activity in hippocampal CA3 circuits
- PMID: 12119362
- PMCID: PMC2173116
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200204066
Mossy fiber Zn2+ spillover modulates heterosynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activity in hippocampal CA3 circuits
Abstract
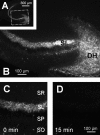
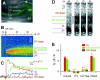
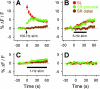
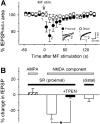
Although Zn2+ is contained in large amounts in the synaptic terminals of hippocampal mossy fibers (MFs), its physiological role in synaptic transmission is poorly understood. By using the newly developed high-sensitivity Zn2+ indicator ZnAF-2, the spatiotemporal dynamics of Zn2+ was monitored in rat hippocampal slices. When high-frequency stimulation was delivered to the MFs, the concentration of extracellular Zn2+ was immediately elevated in the stratum lucidum, followed by a mild increase in the stratum radiatum adjacent to the stratum lucidum, but not in the distal area of stratum radiatum. The Zn2+ increase was insensitive to a non-N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist but was efficiently attenuated by tetrodotoxin or Ca2+-free medium, suggesting that Zn2+ is released by MF synaptic terminals in an activity-dependent manner, and thereafter diffuses extracellularly into the neighboring stratum radiatum. Electrophysiological analyses revealed that NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic responses in CA3 proximal stratum radiatum were inhibited in the immediate aftermath of MF activation and that this inhibition was no longer observed in the presence of a Zn2+-chelating agent. Thus, Zn2+ serves as a spatiotemporal mediator in imprinting the history of MF activity in contiguous hippocampal networks. We predict herein a novel form of metaplasticity, i.e., an experience-dependent non-Hebbian modulation of synaptic plasticity.
Figures
References
-
- Assaf, S.Y., and S.H. Chung. 1984. Release of endogenous Zn2+ from brain tissue during activity. Nature. 308:734–736. - PubMed
-
- Bliss, T.V., and G.L. Collingridge. 1993. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 361:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Brewer, G.J., J.C. Aster, C.A. Knutsen, and W.C. Kruckeberg. 1979. Zinc inhibition of calmodulin: a proposed molecular mechanism of zinc action on cellular functions. Am. J. Hematol. 7:53–60. - PubMed
-
- Choi, D.W., and J.Y. Koh. 1998. Zinc and brain injury. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 21:347–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

