A major susceptibility gene for asthma maps to chromosome 14q24
- PMID: 12119603
- PMCID: PMC379187
- DOI: 10.1086/342205
A major susceptibility gene for asthma maps to chromosome 14q24
Abstract
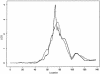
Asthma is a complex genetic disorder with a heterogeneous phenotype, largely attributed to the interactions among many genes and between these genes and the environment. Numerous loci and candidate genes have been reported to show linkage and association to asthma and atopy. Although some studies reporting these observations are compelling, no gene has been mapped that confers a sufficiently high risk of asthma to meet the stringent criteria for genomewide significance. Using 175 extended Icelandic families that included 596 patients with asthma, we performed a genomewide scan with 976 microsatellite markers. The families were identified by cross-matching a list of patients with asthma from the Department of Allergy/Pulmonary Medicine of the National University Hospital of Iceland with a genealogy database of the entire Icelandic nation. We detected linkage of asthma to chromosome 14q24, with an allele-sharing LOD score of 2.66. After we increased the marker density within the locus to an average of one microsatellite every 0.2 cM, the LOD score rose to 4.00. We designate this locus "asthma locus one" (AS1). Taken together, these results provide evidence of a novel susceptibility gene for asthma on chromosome 14q24.
Figures
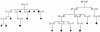

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/
-
- deCODE Genetics Inc., http://www.decode.com/ for deCODE GT program
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for asthma [MIM 600807])
References
-
- American Thoracic Society (1995) Standardization of spirometry, 1994 Update. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152:1107–1136 - PubMed
-
- Bleecker ER, Postma DS, Meyers DA (1997) Evidence for multiple genetic susceptibility loci for asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:S113–S116 - PubMed
-
- Cho SH, Son JW, Koh YY, Min KU, Kim YY, Kim YK (2001) Linkage between bronchial responsiveness to methacholine and gene markers of IL-4 cytokine gene cluster and T-cell receptor α/δ gene complex in Korean nuclear families. Clin Exp Allergy 31:103–109 - PubMed
-
- Cockcroft DW, Killian DN, Mellon JJ, Hargreave FE (1977) Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine: a method and clinical survey. Clin Allergy 7:235–243 - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Asthma, the (1997) A genome-wide search for asthma susceptibility loci in ethnically diverse populations. Nat Genet 15:389–392 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

