Phosphorylation of the postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95)/discs large/zona occludens-1 binding site of stargazin regulates binding to PSD-95 and synaptic targeting of AMPA receptors
- PMID: 12122038
- PMCID: PMC6757934
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-14-05791.2002
Phosphorylation of the postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95)/discs large/zona occludens-1 binding site of stargazin regulates binding to PSD-95 and synaptic targeting of AMPA receptors
Abstract
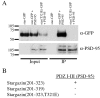
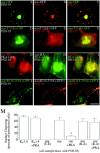
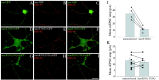
Dynamic regulation of AMPA-type receptors at the synapse is proposed to play a critical role in alterations of the synaptic strength seen in cellular models of learning and memory such as long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Stargazin, previously identified as an AMPA receptor (AMPAR)-interacting protein, is critical for surface expression and synaptic targeting of AMPARs. Stargazin interacts with postsynaptic density-95/discs large/zona occludens-1 (PDZ) proteins via a C-terminal PDZ binding motif. Interestingly, the C terminal of stargazin also predicts phosphorylation at a threonine residue critical for PDZ protein binding. Because protein phosphorylation regulates synaptic plasticity, we characterized this site and the effects of stargazin phosphorylation on AMPAR function. In vitro peptide phosphorylation assays and Western blot analysis with phospho-stargazin-specific antibodies indicate that the critical threonine within the stargazin PDZ binding site is phosphorylated by protein kinase A. This phosphorylation disrupts stargazin interaction and clustering with postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95) in transfected COS-7 cells. Furthermore, a stargazin construct with a Thr-to-Glu mutation that mimics phosphorylation fails to cluster at synaptic spines and downregulates synaptic AMPAR function in cultured hippocampal neurons. These data suggest that phosphorylation of the stargazin PDZ ligand can disrupt stargazin interaction with PSD-95 and thereby regulate synaptic AMPAR function.
Figures

References
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Cao TT, Deacon HW, Reczek D, Bretscher A, von Zastrow M. A kinase-regulated PDZ-domain interaction controls endocytic sorting of the β2-adrenergic receptor. Nature. 1999;401:286–290. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Chetkovich DM, Petrailia RS, Sweeney NT, Kawaski Y, Wenthold R, Bredt DS, Nicoll RA. Stargazin mediates synaptic targeting of AMPA receptors by two distinct mechanisms. Nature. 2000;408:936–943. - PubMed
-
- Choi J, Ko J, Park E, Lee JR, Yoon J, Lim S, Kim E. Phosphorylation of stargazin by PKA regulates its interaction with PSD-95. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:12359–12363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
