Hepatocyte-specific inhibition of NF-kappaB leads to apoptosis after TNF treatment, but not after partial hepatectomy
- PMID: 12122111
- PMCID: PMC151057
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI15295
Hepatocyte-specific inhibition of NF-kappaB leads to apoptosis after TNF treatment, but not after partial hepatectomy
Abstract
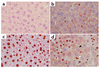
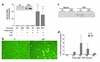
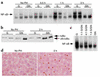
One of the earliest TNF-dependent events to occur during liver regeneration is the activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB through TNF receptor type 1. NF-kappaB activation in the liver can have both antiapoptotic and proliferative effects, but it is unclear which liver cell types, hepatocytes or nonparenchymal cells (NPCs), contribute to these effects. To specifically evaluate the role of hepatocyte NF-kappaB, we created GLVP/DeltaN-IkappaB(alpha) transgenic mice, in which expression of a deletion mutant of IkappaB(alpha) (DeltaN-IkappaB(alpha)) was induced in hepatocytes after injection of mifepristone. In control mice, injection of 25 microg/kg TNF caused NF-kappaB nuclear translocation in virtually all hepatocytes by 30 minutes and no detectable apoptosis, while in mice expressing DeltaN-IkappaB(alpha), NF-kappaB nuclear translocation was blocked in 45% of hepatocytes, leading to apoptosis 4 hours after TNF injection. In contrast, expression of DeltaN-IkappaBalpha in hepatocytes during the first several hours after partial hepatectomy did not lead to apoptosis or decreased proliferation. As NF-kappaB activation was not inhibited in liver NPCs, it is likely that these cells are responsible for mediating the proliferative and antiapoptotic effects of NF-kappaB during liver regeneration.
Figures


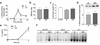
References
-
- Beg AA, Sha WC, Bronson RT, Ghosh S, Baltimore D. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-κB. Nature. 1995;376:167–170. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, et al. NF-kappaB inactivation converts a hepatocyte cell line TNF-alpha response from proliferation to apoptosis. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:C1058–C1066. - PubMed
-
- Kirillova I, Chaisson M, Fausto N. Tumor necrosis factor induces DNA replication in hepatic cells through nuclear factor κB activation. Cell Growth Differ. 1999;10:819–828. - PubMed
-
- Cressman DE, Greenbaum LE, Haber BA, Taub R. Rapid activation of post-hepatectomy factor/nuclear factor kappa B in hepatocytes, a primary response in the regenerating liver. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:30429–30435. - PubMed
-
- FitzGerald MJ, Webber EM, Donovan JR, Fausto N. Rapid DNA binding by nuclear factor kappa B in hepatocytes at the start of liver regeneration. Cell Growth Differ. 1995;6:417–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

