Episodic coronary artery vasospasm and hypertension develop in the absence of Sur2 K(ATP) channels
- PMID: 12122112
- PMCID: PMC151064
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI15672
Episodic coronary artery vasospasm and hypertension develop in the absence of Sur2 K(ATP) channels
Abstract
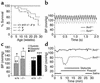
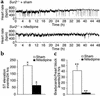
K(ATP) channels couple the intracellular energy state to membrane excitability and regulate a wide array of biologic activities. K(ATP) channels contain a pore-forming inwardly rectifying potassium channel and a sulfonylurea receptor regulatory subunit (SUR1 or SUR2). To clarify the role of K(ATP) channels in vascular smooth muscle, we studied Sur2 gene-targeted mice (Sur2(-/-)) and found significantly elevated resting blood pressures and sudden death. Using in vivo monitoring, we detected transient, repeated episodes of coronary artery vasospasm in Sur2(-/-) mice. Focal narrowings in the coronary arteries were present in Sur2(-/-) mice consistent with vascular spasm. We treated Sur2(-/-) mice with a calcium channel antagonist and successfully reduced vasospastic episodes. The intermittent coronary artery vasospasm seen in Sur2(-/-) mice provides a model for the human disorder Prinzmetal variant angina and demonstrates that the SUR2 K(ATP) channel is a critical regulator of episodic vasomotor activity.
Figures



Comment in
-
The surprising role of vascular K(ATP) channels in vasospastic angina.J Clin Invest. 2002 Jul;110(2):153-4. doi: 10.1172/JCI16122. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12122104 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Noma A. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983;305:147–148. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft SJ, Ashcroft FM. Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal. 1990;2:197–214. - PubMed
-
- Inagaki N, et al. Reconstitution of IKATP: an inward rectifier subunit plus the sulfonylurea receptor. Science. 1995;270:1166–1170. - PubMed
-
- Inagaki N, et al. Cloning and functional characterization of a novel ATP-sensitive potassium channel ubiquitously expressed in rat tissues, including pancreatic islets, pituitary, skeletal muscle, and heart. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:5691–5694. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Bryan L, et al. Cloning of the beta cell high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor: a regulator of insulin secretion. Science. 1995;268:423–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

