Riboflavin is a component of the Na+-pumping NADH-quinone oxidoreductase from Vibrio cholerae
- PMID: 12122213
- PMCID: PMC124912
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.162361299
Riboflavin is a component of the Na+-pumping NADH-quinone oxidoreductase from Vibrio cholerae
Abstract
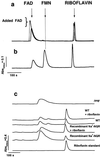
Flavins are cofactors in many electron-transfer enzymes. Typically, two types of flavins perform this role: 5'-phosphoriboflavin (FMN) and flavin-adenine dinucleotide (FAD). Both of these are riboflavin derivatives, but riboflavin itself has never been reported to be an enzyme-bound component. We now report that tightly bound riboflavin is a component of the NADH-driven sodium pump from Vibrio cholerae.
Figures


References
-
- Hayashi M. & Unemoto, T. (1984) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 767, 470-477.
-
- Unemoto T. & Hayashi, M. (1993) J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 25, 385-391. - PubMed
-
- Unemoto T., Akagawa, A. & Hayashi, M. (1993) J. Gen. Microbiol. 139, 2779-2782.
-
- Dibrov P. A., Kostyrko, V. A., Lazarova, R. L., Skulachev, V. P. & Smirnova, I. A. (1986) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 850, 449-457. - PubMed
-
- Kogure K. (1998) Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 9, 278-282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

