Mistargeting hippocampal axons by expression of a truncated Eph receptor
- PMID: 12124402
- PMCID: PMC125042
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.162354599
Mistargeting hippocampal axons by expression of a truncated Eph receptor
Abstract
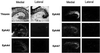
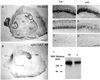
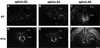
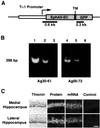
Topographic mapping of axon terminals is a general principle of neural architecture that underlies the interconnections among many neural structures. The Eph family tyrosine kinase receptors and their ligands, the ephrins, have been implicated in the formation of topographic projection maps. We show that multiple Eph receptors and ligands are expressed in the hippocampus and its major subcortical projection target, the lateral septum, and that expression of a truncated Eph receptor in the mouse brain results in a pronounced alteration of the hippocamposeptal topographic map. Our observations provide strong support for a critical role of Eph family guidance factors in regulating ontogeny of hippocampal projections.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential expression of Eph receptors and ephrins correlates with the formation of topographic projections in primary and secondary visual circuits of the embryonic chick forebrain.Dev Biol. 2001 Jun 15;234(2):289-303. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0268. Dev Biol. 2001. PMID: 11397000
-
Complementary and layered expression of Ephs and ephrins in developing mouse inner ear.J Comp Neurol. 2002 Jul 29;449(3):207-16. doi: 10.1002/cne.10231. J Comp Neurol. 2002. PMID: 12115675
-
The EphA4 receptor tyrosine kinase is necessary for the guidance of nasal retinal ganglion cell axons in vitro.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000 Oct;16(4):365-75. doi: 10.1006/mcne.2000.0878. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11085874
-
Roles of Eph receptors and ephrins in segmental patterning.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000 Jul 29;355(1399):993-1002. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0635. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000. PMID: 11128993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the Eph-ephrin signalling system in the regulation of developmental patterning.Int J Dev Biol. 2002;46(4):375-84. Int J Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 12141423 Review.
Cited by
-
Lentiviral vector-mediated gene transfer and RNA silencing technology in neuronal dysfunctions.Mol Biotechnol. 2011 Feb;47(2):169-87. doi: 10.1007/s12033-010-9334-x. Mol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 20862616 Review.
-
Mef2c Controls Postnatal Callosal Axon Targeting by Regulating Sensitivity to Ephrin Repulsion.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 22:2025.01.22.634300. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.22.634300. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Neurosci. 2025 May 21;45(21):e0201252025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0201-25.2025. PMID: 39896513 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Abnormal hippocampal axon bundling in EphB receptor mutant mice.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 10;24(10):2366-74. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4711-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15014111 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of Plexins/Neuropilins and Their Ligands during Hippocampal Development and Neurodegeneration.Cells. 2019 Feb 28;8(3):206. doi: 10.3390/cells8030206. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30823454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopaminergic axon guidance: which makes what?Front Cell Neurosci. 2012 Jul 31;6:32. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2012.00032. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22866028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaas J. H. (1997) Brain Res. Bull. 44, 107-112. - PubMed
-
- Kaas J. H. (1999) in The New Cognitive Neurosciences, ed. Gazzaniga, M. S. (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA), pp. 223–236.
-
- Feldheim D. A., Kim, Y. I., Bergemann, A. D., Frisen, J., Barbacid, M. & Flanagan, J. G. (2000) Neuron 25, 563-574. - PubMed
-
- Udin S. B. & Fawcett, J. W. (1988) Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 289-327. - PubMed
-
- Swanson L. W. & Cowan, W. M. (1977) J. Comp. Neurol. 172, 49-84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

