An instructional program to facilitate teaching joint/soft-tissue injection and aspiration
- PMID: 12133158
- PMCID: PMC1495064
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2002.10310.x
An instructional program to facilitate teaching joint/soft-tissue injection and aspiration
Abstract
Objective: We developed an instructional program to teach aspiration and injection techniques of the knee and shoulder to medical students and residents.
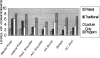
Methods: Residents and fourth-year medical students participating in a rheumatology elective were assigned by deterministic allocation into 3 groups: the Traditional group received no specific instruction in arthrocentesis but simply rotated through rheumatology, learning injection techniques only if they saw patients who required them; the Lecture-only group received only the didactic lecture and did not have the opportunity to practice on the models; the Program group participated in the newly developed program of instruction that combined a didactic lecture and a hands-on workshop using the anatomic models to practice arthrocentesis techniques.
Results: The scores on the written examination for those in the Program group (mean score 37.46 out of 40 possible) and the Lecture-only group (mean 37.75) were significantly higher than those of the Traditional group (mean 33.15) (P <.05). The scores on the practical examination for those in the Program group (mean score 24.08 out of 26 possible) were significantly higher than those of the Lecture-only (mean 20.50) and Traditional (mean 17.33) (P <.05)
Conclusion: The addition of this type of instruction to supplement a traditional internal medicine rotation can enhance a learner's ability to perform joint/soft-tissue injection and aspiration.
Figures
References
-
- Wigton RS, Niolas JA, Blank LL. Procedural skills of the general internist: A survey of 2500 physicians. Ann Intern Med. 1989;111:1023–34. - PubMed
-
- Norris TE, Felmar E, Tolleson G. Which procedures should be currently taught in family practice residency programs. Fam Med. 1997;29:99–104. - PubMed
-
- Wigton RS, Blank LL, Nicolas JA, Tape TG. Procedural skills training in internal medicine residencies: a survey of program directors. Ann Intern Med. 1989;111:932–8. - PubMed
-
- Elnicki DM, Shumway JM, Halbritter KA, Morris DK. Interpretive and procedural skills of the internal medicine clerkship: performance and supervision. South Med J. 1996;89:603–8. - PubMed
-
- Olshaker JS, Brown CK, Arthur DC, Tek D. Animal procedure laboratory surveys: use of the animal laboratory to improve physician confidence and ability. J Emerg Med. 1989;7:593–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources