Novel role of CD8(+) T cells and major histocompatibility complex class I genes in the generation of protective CD4(+) Th1 responses during retrovirus infection in mice
- PMID: 12133998
- PMCID: PMC155146
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.16.7942-7948.2002
Novel role of CD8(+) T cells and major histocompatibility complex class I genes in the generation of protective CD4(+) Th1 responses during retrovirus infection in mice
Abstract
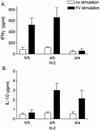
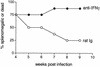
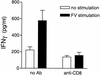
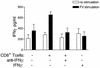
CD4(+) Th1 responses to virus infections are often necessary for the development and maintenance of virus-specific CD8(+) T-cell responses. However, in the present study with Friend murine retrovirus (FV), the reverse was also found to be true. In the absence of a responder H-2(b) allele at major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II loci, a single H-2D(b) MHC class I allele was sufficient for the development of a CD4(+) Th1 response to FV. This effect of H-2D(b) on CD4(+) T-cell responses was dependent on CD8(+) T cells, as demonstrated by depletion studies. A direct effect of CD8(+) T-cell help in the development of CD4(+) Th1 responses to FV was also shown in vaccine studies. Vaccination of nonresponder H-2(a/a) mice induced FV-specific responses of H-2D(d)-restricted CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). Adoptive transfer of vaccine-primed CD8(+) T cells to naive H-2(a/a) mice prior to infection resulted in the generation of FV-specific CD4(+) Th1 responses. This novel helper effect of CD8(+) T cells could be an important mechanism in the development of CD4(+) Th1 responses following vaccinations that induce CD8(+) CTL responses. The ability of MHC class I genes to facilitate CD4(+) Th1 development could also be considerable evolutionary advantage by allowing a wider variety of MHC genotypes to generate protective immune responses against intracellular pathogens.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Major histocompatibility complex class I gene controls the generation of gamma interferon-producing CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells important for recovery from friend retrovirus-induced leukemia.J Virol. 2000 Jun;74(11):5363-7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.11.5363-5367.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10799615 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement for CD4(+) T cells in the Friend murine retrovirus neutralizing antibody response: evidence for functional T cells in genetic low-recovery mice.J Virol. 1998 Nov;72(11):9400-3. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.9400-9403.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9765497 Free PMC article.
-
Host genetic factors that control immune responses to retrovirus infections.Vaccine. 2008 Jun 6;26(24):2981-96. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.01.004. Epub 2008 Jan 22. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18255203 Review.
-
Effects of Friend Virus Infection and Regulatory T Cells on the Antigen Presentation Function of B Cells.mBio. 2019 Jan 22;10(1):e02578-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02578-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30670616 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of nanoparticle-based therapeutic vaccination and transient ablation of regulatory T cells enhances anti-viral immunity during chronic retroviral infection.Retrovirology. 2016 Apr 14;13:24. doi: 10.1186/s12977-016-0258-9. Retrovirology. 2016. PMID: 27076190 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid Functional Decline of Activated and Memory Graft-versus-Host-Reactive T Cells Encountering Host Antigens in the Absence of Inflammation.J Immunol. 2015 Aug 1;195(3):1282-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401511. Epub 2015 Jun 17. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26085679 Free PMC article.
-
beta2-microglobulin-associated regulation of interferon-gamma and virus-specific immunoglobulin G confer resistance against the development of chronic coxsackievirus myocarditis.Am J Pathol. 2003 May;162(5):1709-20. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64305-2. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12707055 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells recognize friend retrovirus-infected erythroid progenitor cells through NKG2D-RAE-1 interactions In Vivo.J Virol. 2011 Jun;85(11):5423-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02146-10. Epub 2011 Mar 16. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21411527 Free PMC article.
-
Vital role for CD8+ cells in controlling retroviral infections.J Virol. 2011 Apr;85(7):3415-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01768-10. Epub 2011 Jan 19. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21248041 Free PMC article.
-
Elimination of friend retrovirus in the absence of CD8+ T cells.J Virol. 2014 Feb;88(3):1854-5. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03271-13. Epub 2013 Nov 13. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24227860 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bancroft, A. J., K. J. Else, and R. K. Grencis. 1994. Low-level infection with Trichuris muris significantly affects the polarization of the CD4 response. Eur. J. Immunol. 24:3113-3118. - PubMed
-
- Blackwell, J. M. 1996. Genetic susceptibility to leishmanial infections: studies in mice and man. Parasitology 112(Suppl.):S67-S74. - PubMed
-
- Bretscher, P. A., G. Wei, J. N. Menon, and H. Bielefeldt-Ohmann. 1992. Establishment of stable, cell-mediated immunity that makes “susceptible” mice resistant to Leishmania major. Science 257:539-542. - PubMed
-
- Cher, D. J., and T. R. Mosmann. 1987. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. II. Delayed-type hypersensitivity is mediated by TH1 clones. J. Immunol. 138:3688-3694. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

