Role of a highly conserved NH(2)-terminal domain of the human parainfluenza virus type 3 RNA polymerase
- PMID: 12134015
- PMCID: PMC155155
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.16.8101-8109.2002
Role of a highly conserved NH(2)-terminal domain of the human parainfluenza virus type 3 RNA polymerase
Abstract
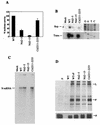
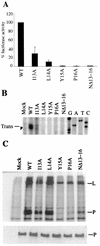
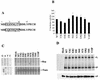
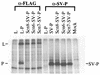
The RNA polymerase complex of human parainfluenza virus type 3 (HPIV 3), a member of the family Paramyxoviridae, is composed of two virally encoded polypeptides: a multifunctional large protein (L, 255 kDa) and a phosphoprotein (P, 90 kDa). From extensive deduced amino acid sequence analyses of the cDNA clones of a number of L proteins of nonsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses, a cluster of high-homology sequence segments have been identified within the body of the L proteins. Here, we have focused on the NH(2)-terminal domain of HPIV 3 L protein that is also highly conserved. Following mutational analyses within this domain, we examined the ability of the mutant L proteins to (i) transcribe an HPIV 3 minireplicon, (ii) transcribe the viral RNA in vitro using the HPIV 3 nucleocapsid RNA template, and (iii) interact with HPIV 3 P protein. Our results demonstrate that the first 15 amino acids of the NH(2)-terminal domain spanning a highly conserved motif is directly involved in transcription of the genome RNA and in forming a functional complex with the P protein. Substitution of eight nonconserved amino acids within this domain by the corresponding Sendai virus L protein residues yielded mutants with variable transcriptional activities. However, one mutant in which all eight amino acids were replaced with the corresponding residues of Sendai virus L protein failed to both transcribe the minireplicon and interact with HPIV 3 P and the Sendai virus P protein. The possible functional significance of the NH(2)-terminal domain of paramyxovirus L protein is discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Banerjee, A. K., S. Barik, and B. P. De. 1991. Gene expression of nonsegmented negative strand RNA viruses. Pharmacol. Ther. 51:47-70. - PubMed
-
- Canter, D. M., R. L, Jackson, and J. Perrault. 1993. Faithful and efficient in vitro reconstitution of vesicular stomatitis virus transcription using plasmid-encoded L and P proteins. Virology 194:518-529. - PubMed
-
- Chandrika, R., S. M. Horikami, S. Smallwood, and S. A. Moyer. 1995. Mutations in conserved domain I of the Sendai virus L polymerase protein uncouple transcription and replication. Virology 213:352-363. - PubMed
-
- Collins, P. L., R. M. Chanock, and K. McIntosh. 1996. Parainfluenza viruses, p. 1205-1241. In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P.M. Howley (ed.), Fields virology, 3rd ed. Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, Pa.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

