The lytic cycle of Epstein-Barr virus is associated with decreased expression of cell surface major histocompatibility complex class I and class II molecules
- PMID: 12134023
- PMCID: PMC155144
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.16.8179-8188.2002
The lytic cycle of Epstein-Barr virus is associated with decreased expression of cell surface major histocompatibility complex class I and class II molecules
Abstract
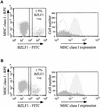
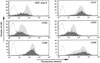
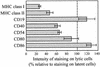
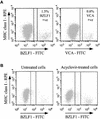
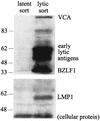
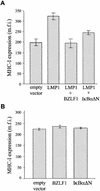
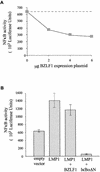
Human herpesviruses utilize an impressive range of strategies to evade the immune system during their lytic replicative cycle, including reducing the expression of cell surface major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and immunostimulatory molecules required for recognition and lysis by virus-specific cytotoxic T cells. Study of possible immune evasion strategies by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in lytically infected cells has been hampered by the lack of an appropriate permissive culture model. Using two-color immunofluorescence staining of cell surface antigens and EBV-encoded lytic cycle antigens, we examined EBV-transformed B-cell lines in which a small subpopulation of cells had spontaneously entered the lytic cycle. Cells in the lytic cycle showed a four- to fivefold decrease in cell surface expression of MHC class I molecules relative to that in latently infected cells. Expression of MHC class II molecules, CD40, and CD54 was reduced by 40 to 50% on cells in the lytic cycle, while no decrease was observed in cell surface expression of CD19, CD80, and CD86. Downregulation of MHC class I expression was found to be an early-lytic-cycle event, since it was observed when progress through late lytic cycle was blocked by treatment with acyclovir. The immediate-early transactivator of the EBV lytic cycle, BZLF1, did not directly affect expression of MHC class I molecules. However, BZLF1 completely inhibited the upregulation of MHC class I expression mediated by the EBV cell-transforming protein, LMP1. This novel function of BZLF1 elucidates the paradox of how MHC class I expression can be downregulated when LMP1, which upregulates MHC class I expression in latent infection, remains expressed in the lytic cycle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Missing Link in Epstein-Barr Virus Immune Evasion: the BDLF3 Gene Induces Ubiquitination and Downregulation of Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I (MHC-I) and MHC-II.J Virol. 2015 Oct 14;90(1):356-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02183-15. Print 2016 Jan 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26468525 Free PMC article.
-
Stage-specific inhibition of MHC class I presentation by the Epstein-Barr virus BNLF2a protein during virus lytic cycle.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Jun;5(6):e1000490. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000490. Epub 2009 Jun 26. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19557156 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus evades CD4+ T cell responses in lytic cycle through BZLF1-mediated downregulation of CD74 and the cooperation of vBcl-2.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Dec;7(12):e1002455. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002455. Epub 2011 Dec 22. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22216005 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus evasion of CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cell immunity via concerted actions of multiple gene products.Semin Cancer Biol. 2008 Dec;18(6):397-408. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.10.008. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008. PMID: 18977445 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 and ZEBRA: targets for therapeutic strategies against EBV-carrying cancers.J Pathol. 2015 Jan;235(2):334-41. doi: 10.1002/path.4431. J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25186125 Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus regulates STAT1 through latent membrane protein 1.J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(7):4439-43. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.7.4439-4443.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12634403 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon regulatory factor 7 is negatively regulated by the Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early gene, BZLF-1.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(15):10040-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.10040-10052.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16014964 Free PMC article.
-
HLA Allele E*01:01 Is Associated with a Reduced Risk of EBV-Related Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma Independently of HLA-A*01/*02.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 11;10(8):e0135512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135512. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26261988 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation between Epstein-Barr virus immune evasion proteins spreads protection from CD8+ T cell recognition across all three phases of the lytic cycle.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Aug 21;10(8):e1004322. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004322. eCollection 2014 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25144360 Free PMC article.
-
The Roseoloviruses Downregulate the Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PTPRC (CD45).J Virol. 2021 Jun 24;95(14):e0162820. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01628-20. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33952641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamson, A. L., D. Darr, E. Holley-Guthrie, R. A. Johnson, A. Mauser, J. Swenson, and S. Kenney. 2000. Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early proteins BZLF1 and BRLF1 activate the ATF2 transcription factor by increasing the levels of phosphorylated p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinases. J. Virol. 74:1224-1233. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

