Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-induced upregulation of the c-kit proto-oncogene, as identified by gene expression profiling, is essential for the transformation of endothelial cells
- PMID: 12134042
- PMCID: PMC155158
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.16.8383-8399.2002
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-induced upregulation of the c-kit proto-oncogene, as identified by gene expression profiling, is essential for the transformation of endothelial cells
Abstract
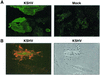
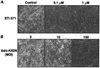
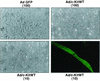
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS), the most frequent malignancy afflicting AIDS patients, is characterized by spindle cell formation and vascularization. Infection with KS-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is consistently observed in all forms of KS. Spindle cell formation can be replicated in vitro by infection of dermal microvascular endothelial cells (DMVEC) with KSHV. To study the molecular mechanism of this transformation, we compared RNA expression profiles of KSHV-infected and mock-infected DMVEC. Induction of several proto-oncogenes was observed, particularly the receptor tyrosine kinase c-kit. Consistent with increased c-Kit expression, KHSV-infected DMVEC displayed enhanced proliferation in response to the c-Kit ligand, stem cell factor (SCF). Inhibition of c-Kit activity with either a pharmacological inhibitor of c-Kit (STI 571) or a dominant-negative c-Kit protein reversed SCF-dependent proliferation. Importantly, inhibition of c-Kit signal transduction reversed the KSHV-induced morphological transformation of DMVEC. Furthermore, overexpression studies showed that c-Kit was sufficient to induce spindle cell formation. Together, these data demonstrate an essential role for c-Kit in KS tumorigenesis and reveal a target for pharmacological intervention.
Figures

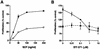
Similar articles
-
A functional genomics approach to Kaposi's sarcoma.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Dec;975:180-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb05951.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12538164
-
Novel cellular genes essential for transformation of endothelial cells by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.Cancer Res. 2005 Jun 15;65(12):5084-95. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2822. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15958552
-
Spindle cell conversion by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: formation of colonies and plaques with mixed lytic and latent gene expression in infected primary dermal microvascular endothelial cell cultures.J Virol. 2001 Jun;75(12):5614-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.12.5614-5626.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11356969 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomics and the development of pathogenesis-targeted therapies for Kaposi's sarcoma.Pharmacogenomics. 2005 Apr;6(3):235-44. doi: 10.1517/14622416.6.3.235. Pharmacogenomics. 2005. PMID: 16013955 Review.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus-induced endothelial cell reprogramming supports viral persistence and contributes to Kaposi's sarcoma tumorigenesis.Curr Opin Virol. 2017 Oct;26:156-162. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Curr Opin Virol. 2017. PMID: 29031103 Review.
Cited by
-
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: immunobiology, oncogenesis, and therapy.J Clin Invest. 2016 Sep 1;126(9):3165-75. doi: 10.1172/JCI84418. Epub 2016 Sep 1. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27584730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular genetics of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus-8) epidemiology and pathogenesis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003 Jun;67(2):175-212, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.2.175-212.2003. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12794189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human herpesvirus-8 infection of primary pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Dec;39(6):706-16. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0368OC. Epub 2008 Jun 27. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18587055 Free PMC article.
-
Phase II trial of imatinib in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma: AIDS Malignancy Consortium Protocol 042.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Feb 10;32(5):402-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.48.6365. Epub 2013 Dec 30. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24378417 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Uncovering the complexities of Kaposi's sarcoma through genome-wide expression analysis.Genome Biol. 2004;5(11):247. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-11-247. Epub 2004 Nov 1. Genome Biol. 2004. PMID: 15535873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allander, S. V., N. N. Nupponen, M. Ringner, G. Hostetter, G. W. Maher, N. Goldberger, Y. Chen, J. Carpten, A. G. Elkahloun, and P. S. Meltzer. 2001. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors with KIT mutations exhibit a remarkably homogeneous gene expression profile. Cancer Res. 61:8624-8628. - PubMed
-
- Aluigi, M. G., A. Albini, S. Carlone, L. Repetto, R. De Marchi, A. Icardi, M. Moro, D. Noonan, and R. Benelli. 1996. KSHV sequences in biopsies and cultured spindle cells of epidemic, iatrogenic and Mediterranean forms of Kaposi's sarcoma. Res. Virol. 147:267-275. - PubMed
-
- Ambroziak, J. A., D. J. Blackbourn, B. G. Herndier, R. G. Glogau, J. H. Gullett, A. R. McDonald, E. T. Lennette, and J. A. Levy. 1995. Herpes-like sequences in HIV-infected and uninfected Kaposi's sarcoma patients. Science 268:582-583. - PubMed
-
- Aoki, Y., E. S. Jaffe, Y. Chang, K. Jones, J. Teruya-Feldstein, P. S. Moore, and G. Tosato. 1999. Angiogenesis and hematopoiesis induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded interleukin-6. Blood 93:4034-4043. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

