Epidermal growth factor receptor dependence of radiation-induced transcription factor activation in human breast carcinoma cells
- PMID: 12134064
- PMCID: PMC117308
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.01-12-0572
Epidermal growth factor receptor dependence of radiation-induced transcription factor activation in human breast carcinoma cells
Abstract
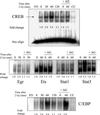
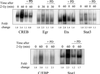
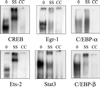
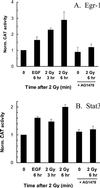
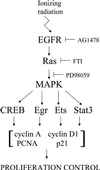
Ionizing radiation (1-5 Gy) activates the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a major effector of the p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. MAPK and its downstream effector, p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (p90RSK), phosphorylate transcription factors involved in cell proliferation. To establish the role of the EGFR/MAPK pathway in radiation-induced transcription factor activation, MDA-MB-231 human breast carcinoma cells were examined using specific inhibitors of signaling pathways. Gel-shift analysis revealed three different profile groups: 1) transcription factors that responded to both radiation (2 Gy) and epidermal growth factor (EGF) (CREB, Egr, Ets, and Stat3); 2) factors that responded to radiation, but not EGF (C/EBP and Stat1); and 3) those that did not respond significantly to either radiation or EGF (AP-1 and Myc). Within groups 1 and 2, a two- to fivefold maximum stimulation of binding activity was observed at 30-60 min after irradiation. Interestingly, only transcription factors that responded to EGF had radiation responses significantly inhibited by the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, AG1478; these responses were also abrogated by farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI) or PD98059, inhibitors of Ras and MEK1/2, respectively. Moreover, radiation-induced increases in CREB and p90RSK phosphorylation and activation of Stat3 and Egr-1 reporter constructs by radiation were all abolished by AG1478. These data demonstrate a distinct radiation response profile at the transcriptional level that is dependent on enhanced EGFR/Ras/MAPK signaling.
Figures





References
-
- Albanese C, Johnson J, Watanabe G, Eklund N, Vu D, Arnold A, Pestell R. Transforming p21ras mutants and c-Ets-2 activate the cyclin D1 promoter through distinguishable regions. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23589–23597. - PubMed
-
- Andrisani OM. CREB-mediated transcriptional control. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1999;9:19–32. - PubMed
-
- Beier F, Taylor AC, LuValle P. The Raf-1/MEK/ERK pathway regulates the expression of the p21(Cip1/Waf1) gene in chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:30273–30279. - PubMed
-
- Beier F, Taylor AC, LuValle P. Activating transcription factor 2 is necessary for maximal activity and serum induction of the cyclin A promoter in chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:12948–12953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

