Statistical significance of clusters of motifs represented by position specific scoring matrices in nucleotide sequences
- PMID: 12136103
- PMCID: PMC135758
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf438
Statistical significance of clusters of motifs represented by position specific scoring matrices in nucleotide sequences
Abstract
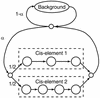
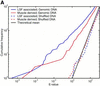
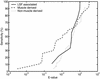
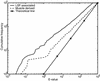
The human genome encodes the transcriptional control of its genes in clusters of cis-elements that constitute enhancers, silencers and promoter signals. The sequence motifs of individual cis- elements are usually too short and degenerate for confident detection. In most cases, the requirements for organization of cis-elements within these clusters are poorly understood. Therefore, we have developed a general method to detect local concentrations of cis-element motifs, using predetermined matrix representations of the cis-elements, and calculate the statistical significance of these motif clusters. The statistical significance calculation is highly accurate not only for idealized, pseudorandom DNA, but also for real human DNA. We use our method 'cluster of motifs E-value tool' (COMET) to make novel predictions concerning the regulation of genes by transcription factors associated with muscle. COMET performs comparably with two alternative state-of-the-art techniques, which are more complex and lack E-value calculations. Our statistical method enables us to clarify the major bottleneck in the hard problem of detecting cis-regulatory regions, which is that many known enhancers do not contain very significant clusters of the motif types that we search for. Thus, discovery of additional signals that belong to these regulatory regions will be the key to future progress.
Figures


References
-
- Lander E.S., Linton,L.M., Birren,B., Nusbaum,C., Zody,M.C., Baldwin,J., Devon,K., Dewar,K., Doyle,M., FitzHugh,W. et al. (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature, 409, 860–921. - PubMed
-
- Claverie J.M., (2000) From bioinformatics to computational biology. Genome Res., 10, 1277–1279. - PubMed
-
- Arnone M.I., and Davidson,E.H. (1997) The hardwiring of development: organization and function of genomic regulatory systems. Development, 124, 1851–1864. - PubMed
-
- Deshler J.O., Highett,M.I. and Schnapp,B.J. (1997) Localization of Xenopus Vg1 mRNA by Vera protein and the endoplasmic reticulum. Science, 276, 1128–1131. - PubMed

