SOX9 interacts with a component of the human thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex
- PMID: 12136106
- PMCID: PMC135763
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf443
SOX9 interacts with a component of the human thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex
Erratum in
- Nucleic Acids Res 2002 Sep 1;30(17):3917. Tibor Schomber [corrected to Schomber Tibor]
Abstract
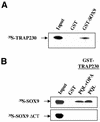
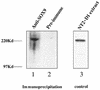
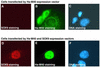
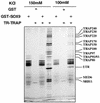
SOX9 transcription factor is involved in chondrocyte differentiation and male sex determination. Heterozygous defects in the human SOX9 gene cause campomelic dysplasia. The mechanisms behind SOX9 function are not understood despite the description of different target genes. This study therefore sets out to identify SOX9-associated proteins to unravel how SOX9 interacts with the cellular transcription machinery. We report the ability of SOX9 to interact with TRAP230, a component of the thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein (TRAP) complex. Both in vitro and in vivo assays have confirmed that the detected interaction is specific and occurs endogenously in cells. Using co-transfection experiments, we have also shown that the TRAP230 interacting domain can act in a dominant-negative manner regarding SOX9 activity. Our results add SOX9 to the list of activators that communicate with the general transcription machinery through the TRAP complex and suggest a basis for the collaboration of SOX9 with different coactivators that could contact the same coactivator/integrator complex.
Figures

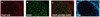
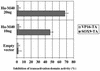
References
-
- Houston C.S., Opitz,J.M., Spranger,J.W., Macpherson,R.I., Reed,M.H., Gilbert,E.F., Herrmann,J. and Schinzel,A. (1983) The campomelic syndrome: review, report of 17 cases, and follow-up on the currently 17-year-old boy first reported by Maroteaux et al in 1971. Am. J. Med. Genet., 15, 3–28. - PubMed
-
- Maroteaux P., Spranger,J., Opitz,J.M., Kucera,J., Lowry,R.B., Schimke,R.N. and Kagan,S.M. (1971) The campomelic syndrome. Presse Med., 79, 1157–1162. - PubMed
-
- Foster J.W., Dominguez-Steglich,M.A., Guioli,S., Kowk,G., Weller,P.A., Stevanovic,M., Weissenbach,J., Mansour,S., Young,I.D., Goodfellow,P.N. et al. (1994) Campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal caused by mutations in an SRY-related gene. Nature, 372, 525–530. - PubMed
-
- Wagner T., Wirth,J., Meyer,J., Zabel,B., Held,M., Zimmer,J., Pasantes,J., Bricarelli,F.D., Keutel,J., Hustert,E. et al. (1994) Autosomal sex reversal and campomelic dysplasia are caused by mutations in and around the SRY-related gene SOX9. Cell, 79, 1111–1120. - PubMed
-
- Meyer J., Sudbeck,P., Held,M., Wagner,T., Schmitz,M.L., Bricarelli,F.D., Eggermont,E., Friedrich,U., Haas,O.A., Kobelt,A. et al. (1997) Mutational analysis of the SOX9 gene in campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal: lack of genotype/phenotype correlations. Hum. Mol. Genet., 6, 91–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

