A pentatricopeptide repeat-containing gene restores fertility to cytoplasmic male-sterile plants
- PMID: 12136123
- PMCID: PMC125068
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.102301599
A pentatricopeptide repeat-containing gene restores fertility to cytoplasmic male-sterile plants
Abstract
Known in over 150 species, cytoplasmic male sterility is encoded by aberrant mitochondrial genes that prevent pollen development. The RNA- or protein-level expression of most of the mitochondrial genes encoding cytoplasmic male sterility is altered in the presence of one or more nuclear genes called restorers of fertility that suppress the male-sterile phenotype. Cytoplasmic male sterility/restorer systems have been proven to be an invaluable tool in the production of hybrid seeds. Despite their importance for both the production of major crops such as rice and sunflower and the study of organelle/nuclear interactions in plants, none of the nuclear fertility-restorer genes that reduce the expression of aberrant mitochondrial proteins have previously been cloned. Here we report the isolation of a gene directly involved in the control of the expression of a cytoplasmic male sterility-encoding gene. The Petunia restorer of fertility gene product is a mitochondrially targeted protein that is almost entirely composed of 14 repeats of the 35-aa pentatricopeptide repeat motif. In a nonrestoring genotype we identified a homologous gene that exhibits a deletion in the promoter region and is expressed in roots but not in floral buds.
Figures
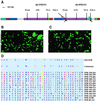
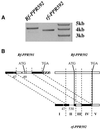
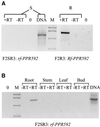
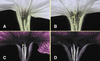

Comment in
-
Nuclear-mediated mitochondrial gene regulation and male fertility in higher plants: Light at the end of the tunnel?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Aug 6;99(16):10240-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.172388899. Epub 2002 Jul 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12149484 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Laser K. D. & Lersten, N. R. (1972) Bot. Rev. 38, 425-454.
-
- Schnable P. S. & Wise, R. P. (1998) Trends Plant Sci. 3, 175-180.
-
- Pruitt K. D. & Hanson, M. R. (1991) Mol. Gen. Genet. 227, 348-355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

