Epstein-Barr virus reactivation after superinfection of the BJAB-B1 and P3HR-1 cell lines with cytomegalovirus
- PMID: 12137568
- PMCID: PMC119847
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-2-20
Epstein-Barr virus reactivation after superinfection of the BJAB-B1 and P3HR-1 cell lines with cytomegalovirus
Abstract
Background: Studies examining herpesvirus-herpesvirus (cytomegalovirus (CMV)-Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)) interactions are limited, and many of the studies have been clinical observations suggesting such an interaction exists. This report aims to examine the in vitro susceptibilities of BJAB-B1 and P3HR-1 cells (EBV positive Burkitt's lymphoma B-cell lines) to a CMV superinfection; and show that EBV reactivation occurs after CMV superinfects these cell lines.
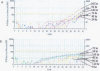
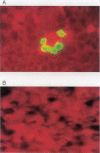
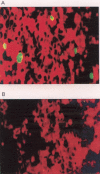
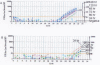
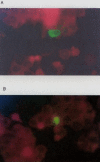
Results: The BJAB-B1 and P3HR-1 cells were observed to be susceptible to a CMV superinfection by detecting the major immediate early (MIE) viral transcript and protein (p52) expression. The BZLF1 transcript was observed in both cell lines superinfected with CMV, indicating EBV reactivation. BZLF1 protein was observed in the BJAB-B1 cells. Antigen detection was not performed in the P3HR-1 cells.
Conclusion: The results from the in vitro superinfections support the in vivo studies suggesting a CMV infection is related to an EBV reactivation and suggests that CMV may be important as a co-factor in EBV pathogenesis in the immunocompromised patient.
Figures


References
-
- Rosenthal KS. Human Herpesviruses. In: Farrell R, editor. Medical Microbiology. St. Louis, Missouri, Mosby-Year Books, Inc; 1994. pp. 571–594.
-
- Bauer G. Induction of Epstein-Barr Virus Early Antigens by Corticosteroids: Inhibition by TPA and Retinoic Acid. Int J Cancer. 1983;31:291–295. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

