Regulation of alternative splicing by the ATP-dependent DEAD-box RNA helicase p72
- PMID: 12138182
- PMCID: PMC133985
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.16.5698-5707.2002
Regulation of alternative splicing by the ATP-dependent DEAD-box RNA helicase p72
Abstract
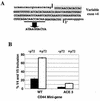
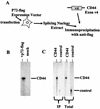
Although a number of ATP-dependent RNA helicases are important for constitutive RNA splicing, no helicases have been implicated in alternative RNA splicing. Here, we show that the abundant DEAD-box RNA helicase p72, but not its close relative p68, affects the splicing of alternative exons containing AC-rich exon enhancer elements. The effect of p72 was tested by using mini-genes that undergo different types of alternative splicing. When the concentration of p72 was increased in transient transfections, the inclusion of enhancer-containing CD44 alternative exons v4 and v5 increased using a mini-gene that contained these exons and their flanking introns inserted into a beta-globin gene. Other types of alternative splicing were not impacted by altering p72 concentrations. Mutation of the p72 helicase ATP-binding site or deletion of the carboxy-terminal region of the protein reduced the ability of the transfected protein to affect CD44 variable exon splicing. Use of in vitro extracts overexpressing p72 indicated that p72 becomes associated with complexes containing precursor RNA. Helicases have been implicated both in altering RNA-RNA interactions and in remodeling RNA-protein complexes. CD44 exon v4 contains a potential internal secondary structure element that base pairs the 5' splice site with a region inside the exon located between enhancer elements. Mutations that destroyed this complementarity modestly increased inclusion in the absence of p72 but still responded to increasing p72 concentration like the wild-type exon, suggesting that p72 might have effects on protein-RNA interactions. In agreement with this hypothesis, p72 was not able to restore the inclusion of an exon mutated for its major enhancer element. Our results suggest that RNA helicases may be important alternative splicing regulatory factors.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The mRNA of DEAD box protein p72 is alternatively translated into an 82-kDa RNA helicase.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jan 11;277(2):1066-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107535200. Epub 2001 Oct 23. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11675387
-
Rearrangement of structured RNA via branch migration structures catalysed by the highly related DEAD-box proteins p68 and p72.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 May 15;29(10):2088-96. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.10.2088. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11353078 Free PMC article.
-
The highly related DEAD box RNA helicases p68 and p72 exist as heterodimers in cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Mar 1;31(5):1470-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg236. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12595555 Free PMC article.
-
A new twist on RNA helicases: DExH/D box proteins as RNPases.Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Feb;8(2):113-6. doi: 10.1038/84091. Nat Struct Biol. 2001. PMID: 11175897 Review.
-
The DEAD-box protein family of RNA helicases.Gene. 2006 Feb 15;367:17-37. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.10.019. Epub 2005 Dec 7. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16337753 Review.
Cited by
-
Conserved RNA-binding proteins required for dendrite morphogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans sensory neurons.G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Feb 10;5(4):639-53. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.017327. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 25673135 Free PMC article.
-
The p68 and p72 DEAD box RNA helicases interact with HDAC1 and repress transcription in a promoter-specific manner.BMC Mol Biol. 2004 Aug 6;5:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-5-11. BMC Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15298701 Free PMC article.
-
Solution structure of the pseudo-5' splice site of a retroviral splicing suppressor.RNA. 2004 Sep;10(9):1388-98. doi: 10.1261/rna.7020804. RNA. 2004. PMID: 15317975 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing in action: assessing disease causing sequence changes.J Med Genet. 2005 Oct;42(10):737-48. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2004.029538. J Med Genet. 2005. PMID: 16199547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Helicase DDX17 Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Blocking Viral Pregenomic RNA Encapsidation.J Virol. 2021 Sep 9;95(19):e0044421. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00444-21. Epub 2021 Sep 9. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34287051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caruthers, J. M., and D. B. McKay. 2002. Helicase structure and mechanism. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12:123-133. - PubMed
-
- Chen, J. Y., L. Stands, J. P. Staley, R. R. Jackups, L. J. Latus, and T. H. Chang. 2001. Specific alterations of U1-C protein or U1 small nuclear RNA can eliminate the requirement of Prp28p, an essential DEAD box splicing factor. Mol. Cell 7:227-232. - PubMed
-
- de la Cruz, J., D. Kressler, and P. Linder. 1999. Unwinding RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: DEAD-box proteins and related families. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24:192-199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
