Human papillomavirus oncoprotein E6 inactivates the transcriptional coactivator human ADA3
- PMID: 12138191
- PMCID: PMC133989
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.16.5801-5812.2002
Human papillomavirus oncoprotein E6 inactivates the transcriptional coactivator human ADA3
Abstract
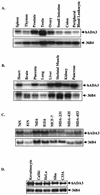
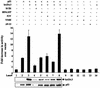
High-risk human papillomaviruses (HPVs) are associated with carcinomas of the cervix and other genital tumors. The HPV oncoprotein E6 is essential for oncogenic transformation. We identify here hADA3, human homologue of the yeast transcriptional coactivator yADA3, as a novel E6-interacting protein and a target of E6-induced degradation. hADA3 binds selectively to the high-risk HPV E6 proteins and only to immortalization-competent E6 mutants. hADA3 functions as a coactivator for p53-mediated transactivation by stabilizing p53 protein. Notably, three immortalizing E6 mutants that do not induce direct p53 degradation but do interact with hADA3 induced the abrogation of p53-mediated transactivation and G(1) cell cycle arrest after DNA damage, comparable to wild-type E6. These findings reveal a novel strategy of HPV E6-induced loss of p53 function that is independent of direct p53 degradation. Given the likely role of the evolutionarily conserved hADA3 in multiple coactivator complexes, inactivation of its function may allow E6 to perturb numerous cellular pathways during HPV oncogenesis.
Figures





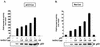
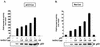
Similar articles
-
Human papilloma virus 16 E6 oncoprotein inhibits retinoic X receptor-mediated transactivation by targeting human ADA3 coactivator.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 22;277(47):45611-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208447200. Epub 2002 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12235159
-
hAda3 degradation by papillomavirus type 16 E6 correlates with abrogation of the p14ARF-p53 pathway and efficient immortalization of human mammary epithelial cells.J Virol. 2008 Apr;82(8):3912-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02466-07. Epub 2008 Feb 6. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18256148 Free PMC article.
-
Human ADA3 binds to estrogen receptor (ER) and functions as a coactivator for ER-mediated transactivation.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 24;279(52):54230-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404482200. Epub 2004 Oct 20. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15496419
-
Regulation of cell cycle progression and apoptosis by the papillomavirus E6 oncogene.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2004;14(3):183-202. doi: 10.1615/critreveukaryotgeneexpr.v14.i3.30. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2004. PMID: 15248815 Review.
-
Tale of a multifaceted co-activator, hADA3: from embryogenesis to cancer and beyond.Open Biol. 2016 Sep;6(9):160153. doi: 10.1098/rsob.160153. Open Biol. 2016. PMID: 27605378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immortalization of human mammary epithelial cells is associated with inactivation of the p14ARF-p53 pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Mar;24(5):2144-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.2144-2152.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14966292 Free PMC article.
-
Activated Notch1 inhibits p53-induced apoptosis and sustains transformation by human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncogenes through a PI3K-PKB/Akt-dependent pathway.J Virol. 2003 Jun;77(12):7106-12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.12.7106-7112.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12768030 Free PMC article.
-
The human papillomavirus 16 E6 protein can either protect or further sensitize cells to TNF: effect of dose.Cell Death Differ. 2005 Dec;12(12):1622-35. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401678. Epub 2005 Jun 3. Cell Death Differ. 2005. PMID: 15933739 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer subtypes: two decades of journey from cell culture to patients.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;720:135-44. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0254-1_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21901624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 to E6AP is not required for activation of hTERT.J Virol. 2008 Jan;82(1):71-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01776-07. Epub 2007 Oct 17. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 17942561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali, S. H., and J. A. DeCaprio. 2001. Cellular transformation by SV40 large T antigen: interaction with host proteins. Semin. Cancer Biol. 11:15-23. - PubMed
-
- Allan, L. A., and M. Fried. 1999. p53-dependent apoptosis or growth arrest induced by different forms of radiation in U2OS cells: p21WAF1/CIP1 repression in UV-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 18:5403-5412. - PubMed
-
- Anafi, M., Y. F. Yang, N. A. Barlev, M. V. Govindan, S. L. Berger, T. R. Butt, and P. G. Walfish. 2000. GCN5 and ADA adaptor proteins regulate triiodothyronine/GRIP1 and SRC-1 coactivator-dependent gene activation by the human thyroid hormone receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 14:718-732. - PubMed
-
- Avantaggiati, M. L., V. Ogryzko, K. Gardner, A. Giordano, A. S. Levine, and K. Kelly. 1997. Recruitment of p300/CBP in p53-dependent signal pathways. Cell 89:1175-1184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
