The gene expression sequence of radiated mucosa in an animal mucositis model
- PMID: 12139712
- PMCID: PMC6496665
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2184.35.s1.10.x
The gene expression sequence of radiated mucosa in an animal mucositis model
Abstract
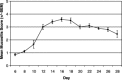
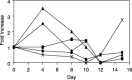
Oral mucositis is a common, dose-limiting, acute toxicity of radiation therapy administered for the treatment of cancers of the head and neck. Accumulating data would suggest that the pathogenesis of mucositis is complex and involves the sequential interaction of all cell types of the oral mucosa, as well as a number of cytokines and elements of the oral environment. While a number of studies have reported on gene expression of particular cell types in response to radiation, the overall response of irradiated mucosa has only been evaluated in a limited way. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the expression of a target group of genes using RNA quantification assays and, more broadly, to assess patterns of mucosal gene expression using DNA microarray hybridization. Our results demonstrate the sequential upregulation of a series of genes that, when taken collectively, suggest an intricate functional interaction.
Figures
References
-
- Bayerl C, Taake S, Moll I, Jung EG (1995) Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 11, 149. - PubMed
-
- Bours V, Bentires‐Alj M, Hellin AC, Viatour P, Robe P, Dalhalle S, Benoit V, Merville MP (2000) Nuclear factor‐kappaB, cancer, and apoptosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 60, 1085. - PubMed
-
- De Toledo SM, Azzam EI, Keng P, Laffrenier S, Little JB (1998) Regulation by ionizing radiation of CDC2, cyclin A, cyclin B, thymidine kinase, topoisomerase IIalpha, and RAD51 expression in normal human diploid fibroblasts is dependent on p53/p21Wafl . Cell Growth Differ. 9, 887. - PubMed
-
- Gilles C, Polette M, Zahm J, Tournier J, Volders L, Foldart J, Birembaut P (1999) Vimentin contributes to human mammary epithelial cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 112, 4615. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

