Contact order and ab initio protein structure prediction
- PMID: 12142448
- PMCID: PMC2373674
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.3790102
Contact order and ab initio protein structure prediction
Abstract
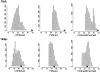
Although much of the motivation for experimental studies of protein folding is to obtain insights for improving protein structure prediction, there has been relatively little connection between experimental protein folding studies and computational structural prediction work in recent years. In the present study, we show that the relationship between protein folding rates and the contact order (CO) of the native structure has implications for ab initio protein structure prediction. Rosetta ab initio folding simulations produce a dearth of high CO structures and an excess of low CO structures, as expected if the computer simulations mimic to some extent the actual folding process. Consistent with this, the majority of failures in ab initio prediction in the CASP4 (critical assessment of structure prediction) experiment involved high CO structures likely to fold much more slowly than the lower CO structures for which reasonable predictions were made. This bias against high CO structures can be partially alleviated by performing large numbers of additional simulations, selecting out the higher CO structures, and eliminating the very low CO structures; this leads to a modest improvement in prediction quality. More significant improvements in predictions for proteins with complex topologies may be possible following significant increases in high-performance computing power, which will be required for thoroughly sampling high CO conformations (high CO proteins can take six orders of magnitude longer to fold than low CO proteins). Importantly for such a strategy, simulations performed for high CO structures converge much less strongly than those for low CO structures, and hence, lack of simulation convergence can indicate the need for improved sampling of high CO conformations. The parallels between Rosetta simulations and folding in vivo may extend to misfolding: The very low CO structures that accumulate in Rosetta simulations consist primarily of local up-down beta-sheets that may resemble precursors to amyloid formation.
Figures

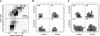


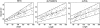
References
-
- Baldwin, R.L. and Rose, G.D. 1999. Is protein folding hierarchic? II: Folding intermediates and transition states. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24 77–83. - PubMed
-
- Bonneau, R., Strauss, C.E.M., and Baker, D. 2001. Improving the performance of ROSETTA using multiple sequence alignment information and global measures of hydrophobic core formation. Proteins 43 1–11. - PubMed
-
- Bonneau, R., Tsai, J., Ruczinski, I., and Baker, D. 2001a. Functional inferences from blind ab initio protein structure predictions. J. Struct. Biol. 134 186–190. - PubMed
-
- Bonneau, R, Tsai, J., Ruczinski, I., Chivian, D., Rohl, C., Strauss, C.E.M., and Baker, D. 2001b. Rosetta in CASP4: Progress in ab initio protein structure prediction. Proteins 45 119–126. - PubMed
-
- Bowers, P.M., Strauss, C.E., and Baker, D. 2000. De novo protein structure determination using sparse NMR data. J. Biomol. NMR 18 311–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

