TNF-alpha, inefficient by itself, potentiates IL-1beta-induced PGHS-2 expression in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells: requirement of NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK pathways
- PMID: 12145100
- PMCID: PMC1573439
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704811
TNF-alpha, inefficient by itself, potentiates IL-1beta-induced PGHS-2 expression in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells: requirement of NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK pathways
Abstract
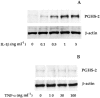
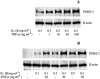
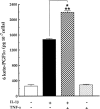
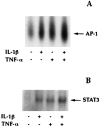
1: Prostaglandin H synthase-2 (PGHS-2), is an inducible enzyme involved in various inflammatory responses. We established here that interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) but not tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) increased its expression in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMEC). However, associated with IL-1beta, TNF-alpha greatly potentiated this enzyme induction. 2: Although unable to induce PGHS-2 expression by itself, TNF-alpha promoted a similar transcription nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation to IL-1beta. This effect was more pronounced when cells were co-exposed to both cytokines. HPMEC pre-treatment with MG-132, a proteasome inhibitor, prevented NF-kappaB activation as well as more distal signalling response, indicating that NF-kappaB activation is required but not sufficient for PGHS-2 expression. 3: Both IL-1beta and TNF-alpha failed to activate c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK). In addition, PD98059, a p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation inhibitor, did not decrease PGHS-2 expression. However, SB 203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor, suppressed PGHS-2 induction by IL-1beta alone or combined with TNF-alpha, demonstrating that p38 MAPK but not p42/44 MAPK or JNK cascades are required for PGHS-2 up-regulation. 4: Finally, TNF-alpha, unlike IL-1beta, was unable to promote p38 MAPK phosphorylation, indicating that the failure of TNF-alpha to induce PGHS-2 expression is linked, at least in part, to its inability to activate p38 MAPK signalling pathway. Altogether, these data enhanced our understanding of PGHS-2 regulation in HPMEC and emphasize the heterogeneity of cellular responses to proinflammatory cytokines.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibition by eicosapentaenoic acid of IL-1beta-induced PGHS-2 expression in human microvascular endothelial cells: involvement of lipoxygenase-derived metabolites and p38 MAPK pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 Feb 20;1631(1):77-84. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(02)00358-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. PMID: 12573452
-
Genetic deletion of PKR abrogates TNF-induced activation of IkappaBalpha kinase, JNK, Akt and cell proliferation but potentiates p44/p42 MAPK and p38 MAPK activation.Oncogene. 2007 Feb 22;26(8):1201-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209906. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 16924232
-
Activation of p38, ERK1/2 and NIK pathways is required for IL-1beta and TNF-alpha-induced chemokine expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2001 Jul;73(1):111-21. doi: 10.1006/exer.2001.1019. Exp Eye Res. 2001. PMID: 11428868
-
The effect of reactive oxygen species on the synthesis of prostanoids from arachidonic acid.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;64(4):409-21. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24101387 Review.
-
TNF-alpha/IL-1/NF-kappaB transduction pathway in human cancer prostate.Histol Histopathol. 2008 Oct;23(10):1279-90. doi: 10.14670/HH-23.1279. Histol Histopathol. 2008. PMID: 18712680 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of src-suppressed C kinase substrate in rat pulmonary microvascular endothelial hyperpermeability stimulated by inflammatory cytokines.Inflamm Res. 2010 Nov;59(11):949-58. doi: 10.1007/s00011-010-0207-3. Epub 2010 May 8. Inflamm Res. 2010. PMID: 20454828
-
Maternal nano-titanium dioxide inhalation exposure alters placental cyclooxygenase and oxidant balance in a sexually dimorphic manner.Adv Redox Res. 2024 Apr;10:10.1016/j.arres.2023.100090. doi: 10.1016/j.arres.2023.100090. Adv Redox Res. 2024. PMID: 38562524 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory responses in primary muscle cell cultures in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar).BMC Genomics. 2013 Nov 1;14:747. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-747. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24180744 Free PMC article.
-
Prostacyclin release and receptor activation: differential control of human pulmonary venous and arterial tone.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Jun;142(4):788-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705843. Epub 2004 Jun 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15172959 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial TNF-α induction by Hsp60 secreted from THP-1 monocytes exposed to hyperglycaemic conditions.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018 Jul;23(4):519-525. doi: 10.1007/s12192-017-0858-x. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018. PMID: 29134442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALLPORT V.C., SLATER D.M., NEWTON R., BENNETT P.R. NF-kappaB and AP-1 are required for cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression in amnion epithelial cell line (WISH) Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2000;6:561–565. - PubMed
-
- BIDGOOD M.J., JAMAL O.S., CUNNINGHAM A.M., BROOKS P.M., SCOTT K.F. Type IIA secretory phospholipase A2 up-regulates cyclo-oxygenase-2 and amplifies cytokine-mediated prostaglandin production in human rheumatoid synoviocytes. J. Immunol. 2000;165:2790–2797. - PubMed
-
- BOULTON T.G., NYE S.H., ROBBINS D.J., IP N.Y., RADZIEJEWSKA E., MORGENBESSER S.D., DEPINHO R.A., PANAYOTATOS N., COBB M.H., YANCOPOULOS G.D. Nucleotide, OMIM, Protein ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991;65:663–675. - PubMed
-
- CHEN C.C., SUN Y.T., CHEN J.J., CHANG Y.J. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression via sequential activation of ceramide-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinases, and IkappaB kinase 1/2 in human alveolar epithelial cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001;59:493–500. - PubMed
-
- CHEN C.C., SUN Y.T., CHEN J.J., CHIU K.T. TNF-α-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human lung epithelial cells: involvement of the phospholipase C-γ2, protein kinase C-α, tyrosine kinase, NF-κB-inducing kinase, and I-κB kinase 1/2 pathway. J. Immunol. 2000;165:2719–2728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

