M-LDH serves as a sarcolemmal K(ATP) channel subunit essential for cell protection against ischemia
- PMID: 12145195
- PMCID: PMC126135
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf388
M-LDH serves as a sarcolemmal K(ATP) channel subunit essential for cell protection against ischemia
Abstract
ATP-sensitive K(+) (K(ATP)) channels in the heart are normally closed by high intracellular ATP, but are activated during ischemia to promote cellular survival. These channels are heteromultimers composed of Kir6.2 subunit, an inwardly rectifying K(+) channel core, and SUR2A, a regulatory subunit implicated in ligand-dependent regulation of channel gating. Here, we have shown that the muscle form (M-LDH), but not heart form (H-LDH), of lactate dehydrogenase is directly physically associated with the sarcolemmal K(ATP) channel by interacting with the Kir6.2 subunit via its N-terminus and with the SUR2A subunit via its C-terminus. The species of LDH bound to the channel regulated the channel activity despite millimolar concentration of intracellular ATP. The presence of M-LDH in the channel protein complex was required for opening of K(ATP) channels during ischemia and ischemia-resistant cellular phenotype. We conclude that M-LDH is an integral part of the sarcolemmal K(ATP) channel protein complex in vivo, where, by virtue of its catalytic activity, it couples the metabolic status of the cell with the K(ATP) channels activity that is essential for cell protection against ischemia.
Figures

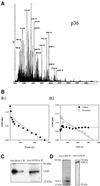
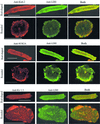
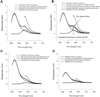






References
-
- Altschuld R.A., Jung,D.W., Phillips,R.M., Narayan,P., Castillo,L.C., Whitaker,T.E., Hensley,J., Hohl,C.M. and Brierley,G.P. (1994) Evidence against norepinephrine-stimulated efflux of mitochondrial Mg2+ from intact cardiac myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 266, H1103–H1111. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft F.M. and Gribble,F.M. (1998) Correlating structure and function in ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Trends Neurosci., 21, 288–294. - PubMed
-
- Clarke A.R., Wigley,D.B., Chia,W.N., Barstow,D., Atkinson,T. and Holbrook,J.J. (1986) Site-directed mutagenesis reveals role of mobile arginine residue in lactate dehydrogenase catalysis. Nature, 324, 699–702. - PubMed
-
- Clegg R.M. (1992) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer and nucleic acids. Methods Enzymol., 211, 353–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

