Localization of the yeast RNA polymerase I-specific subunits
- PMID: 12145213
- PMCID: PMC126139
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf392
Localization of the yeast RNA polymerase I-specific subunits
Abstract
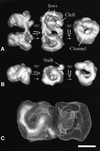
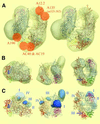
The spatial distribution of four subunits specifically associated to the yeast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase I (RNA pol I) was studied by electron microscopy. A structural model of the native enzyme was determined by cryo-electron microscopy from isolated molecules and was compared with the atomic structure of RNA pol II Delta 4/7, which lacks the specific polypeptides. The two models were aligned and a difference map revealed four additional protein densities present in RNA pol I, which were characterized by immunolabelling. A protruding protein density named stalk was found to contain the RNA pol I-specific subunits A43 and A14. The docking with the atomic structure showed that the stalk protruded from the structure at the same site as the C-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA pol II. Subunit A49 was placed on top of the clamp whereas subunit A34.5 bound at the entrance of the DNA binding cleft, where it could contact the downstream DNA. The location of the RNA pol I-specific subunits is correlated with their biological activity.
Figures



References
-
- Buhler J.M., Huet,J., Davies,K.E., Sentenac,A. and Fromageot,P. (1980) Immunological studies of yeast nuclear RNA polymerases at the subunit level. J. Biol. Chem., 255, 9949–9954. - PubMed
-
- Cramer P., Bushnell,D.A. and Kornberg,R.D. (2001) Structural basis of transcription: RNA polymerase II at 2.8 Å resolution. Science, 292, 1863–1876. - PubMed
-
- Darst S.A., Edwards,A.M., Kubalek,E.W. and Kornberg,R.D. (1991) Three-dimensional structure of yeast RNA polymerase II at 16 Å resolution. Cell, 66, 121–128. - PubMed
-
- Dumay H., Rubbi,L., Sentenac,A. and Marck,C. (1999) Interaction between yeast RNA polymerase III and transcription factor TFIIIC via ABC10α and τ131 subunits. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 33462–33468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

