Accumulation of inorganic polyphosphate in phoU mutants of Escherichia coli and Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803
- PMID: 12147514
- PMCID: PMC124021
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.8.4107-4110.2002
Accumulation of inorganic polyphosphate in phoU mutants of Escherichia coli and Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803
Abstract
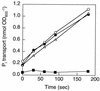
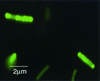
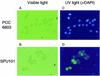
The biological process for phosphate (P(i)) removal is based on the use of bacteria capable of accumulating inorganic polyphosphate (polyP). We obtained Escherichia coli mutants which accumulate a large amount of polyP. The polyP accumulation in these mutants was ascribed to a mutation of the phoU gene that encodes a negative regulator of the P(i) regulon. Insertional inactivation of the phoU gene also elevated the intracellular level of polyP in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. The mutant could remove fourfold more P(i) from the medium than the wild-type strain removed.
Figures
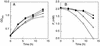
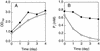
Similar articles
-
Stable polyphosphate accumulation by a pseudo-revertant of an Escherichia coli phoU mutant.Biotechnol Lett. 2013 May;35(5):695-701. doi: 10.1007/s10529-012-1133-y. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Biotechnol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23288295
-
Inorganic polyphosphate in Escherichia coli: the phosphate regulon and the stringent response.J Bacteriol. 1998 Apr;180(8):2186-93. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.8.2186-2193.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9555903 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Polyphosphate Degradation in Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 through Inactivation of the phoU Gene.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 28;34(2):407-414. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2311.11046. Epub 2024 Jan 8. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38247220 Free PMC article.
-
Control of the phoBR Regulon in Escherichia coli.EcoSal Plus. 2019 Sep;8(2):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0006-2019. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0006-2019. EcoSal Plus. 2019. PMID: 31520469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inorganic polyphosphate regulates responses of Escherichia coli to nutritional stringencies, environmental stresses and survival in the stationary phase.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1999;23:183-95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-58444-2_9. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10448677 Review.
Cited by
-
Accumulation of polyphosphate in Lactobacillus spp. and its involvement in stress resistance.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Mar;80(5):1650-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03997-13. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24375133 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the PhoB Regulon and Role of PhoU in the Phosphate Starvation Response of Caulobacter crescentus.J Bacteriol. 2015 Oct 19;198(1):187-200. doi: 10.1128/JB.00658-15. Print 2016 Jan 1. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26483520 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the biosynthesis and functionality of polyphosphate in Bifidobacterium longum KABP042.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 8;13(1):11076. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38082-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37422465 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Phosphate Sensing, Transport and Signalling in Streptomyces and Related Actinobacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 23;22(3):1129. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031129. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33498785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The quantitative proteomic response of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 to phosphate acclimation.Aquat Biosyst. 2013 Feb 26;9(1):5. doi: 10.1186/2046-9063-9-5. Aquat Biosyst. 2013. PMID: 23442353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama, M., E. Crooke, and A. Kornberg. 1992. The polyphosphate kinase gene of Escherichia coli. Isolation and sequence of the ppk gene and membrane location of the protein. J. Biol. Chem. 267:22556-22561. - PubMed
-
- Allan, R. A., and J. J. Miller. 1980. Influence of S-adenosylmethionine on DAPI-induced fluorescence of polyphosphate in the yeast vacuole. Can. J. Microbiol. 26:912-920. - PubMed
-
- Amemura, M., K. Makino, H. Shinagawa, A. Kobayashi, and A. Nakata. 1985. Nucleotide sequence of the genes involved in phosphate transport and regulation of the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 20:241-250. - PubMed
-
- Berlyn, M. K. B., K. B. Low, and K. E. Rudd. 1996. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, p. 1715-1902. In F. C. Neidhardt, R. Curtiss III, J. L. Ingraham, E. C. C. Lin, K. B. Low, B. Magasanik, W. S. Reznikoff, M. Riley, M. Schaechter, and H. E. Umbarger (ed.), Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology, 2nd ed. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

