Sodium dodecyl sulfate hypersensitivity of clpP and clpB mutants of Escherichia coli
- PMID: 12147516
- PMCID: PMC124035
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.8.4117-4121.2002
Sodium dodecyl sulfate hypersensitivity of clpP and clpB mutants of Escherichia coli
Abstract
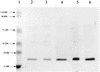
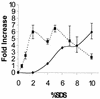
We studied the hypersensitivity of clpP and clpB mutants of Escherichia coli to sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Both wild-type E. coli MC4100 and lon mutants grew in the presence of 10% SDS, whereas isogenic clpP and clpB single mutants could not grow above 0.5% SDS and clpA and clpX single mutants could not grow above 5.0% SDS. For wild-type E. coli, cellular ClpP levels as determined by Western immunoblot analysis increased ca. sixfold as the levels of added SDS increased from 0 to 2%. Capsular colanic acid, measured as uronic acid, increased ca. sixfold as the levels of added SDS increased from 2 to 10%. Based on these findings, 3 of the 19 previously identified SDS shock proteins (M. Adamowicz, P. M. Kelley, and K. W. Nickerson, J. Bacteriol. 173:229-233, 1991) are tentatively identified as ClpP, ClpX, and ClpB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ClpX, an alternative subunit for the ATP-dependent Clp protease of Escherichia coli. Sequence and in vivo activities.J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22618-26. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 8226770
-
Global transcriptional analysis of clpP mutations of type 2 Streptococcus pneumoniae and their effects on physiology and virulence.J Bacteriol. 2002 Jul;184(13):3508-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.13.3508-3520.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12057945 Free PMC article.
-
Global role for ClpP-containing proteases in stationary-phase adaptation of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2003 Jan;185(1):115-25. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.1.115-125.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12486047 Free PMC article.
-
ATP-dependent proteases that also chaperone protein biogenesis.Trends Biochem Sci. 1997 Apr;22(4):118-23. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(97)01020-7. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997. PMID: 9149530 Review.
-
Pathways of protein remodeling by Escherichia coli molecular chaperones.Genet Eng (N Y). 1996;18:203-17. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1766-9_12. Genet Eng (N Y). 1996. PMID: 8785122 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Survey of extreme solvent tolerance in gram-positive cocci: membrane fatty acid changes in Staphylococcus haemolyticus grown in toluene.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Sep;71(9):5171-6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.9.5171-5176.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16151101 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically Programmable Self-Regenerating Bacterial Hydrogels.Adv Mater. 2019 Oct;31(40):e1901826. doi: 10.1002/adma.201901826. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 31402514 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic modulation of capsular exopolysaccharide and virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Feb 13;11(2):e1004691. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004691. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25679516 Free PMC article.
-
Starvation induces shrinkage of the bacterial cytoplasm.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jun 15;118(24):e2104686118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2104686118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34117124 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfate Ester Detergent Degradation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Is Subject to both Positive and Negative Regulation.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Nov 14;85(23):e01352-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01352-19. Print 2019 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31540990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aspedon, A., and K. W. Nickerson. 1993. A two-part energy burden imposed by growth of Enterobacter cloacae and Escherichia coli in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Can. J. Microbiol. 39:555-561. - PubMed
-
- Aspedon, A., and K. W. Nickerson. 1994. The energy dependence of detergent resistance in Enterobacter cloacae: a likely requirement for ATP rather than a proton gradient or a membrane potential. Can. J. Microbiol. 40:184-191. - PubMed
-
- Blumenkrantz, N., and G. Hansen-Asboe. 1973. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal. Biochem. 54:484-489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

