Alterations of the MDV oncogenic regions in an MDV transformed lymphoblastoid cell line
- PMID: 12147717
- PMCID: PMC1187189
- DOI: 10.1136/mp.55.4.262
Alterations of the MDV oncogenic regions in an MDV transformed lymphoblastoid cell line
Abstract
Aims: Lymphoblastoid cell lines derived from Marek's disease virus (MDV) induced tumours have served as models of MDV latency and transformation. They are stable and can be cultured with no detectable MDV genomic alterations upon repeated passaging. An MDV transformed lymphoblastoid T cell line (T9 cell line) has been reported to contain a disrupted MDV BamHI-H fragment and a Rous associated virus insertional activation of the c-myb protooncogene. In an attempt to define the respective participation of c-myb and MDV in the transformed phenotype of T9 cells, an analysis of MDV oncogenic sequences (BamHI-H, BamHI-A, and EcoQ fragments) was performed in these cells.
Methods: Using two different passages of the T9 cell line (late and early passages), the organisation of the MDV oncogenic regions and their expression in these cells were analysed. In vivo assessment of the oncogenicity of the virus contained within these cells was assessed by injecting them into 1 day old chickens.
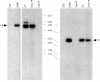
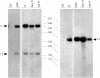
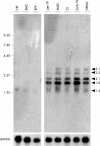
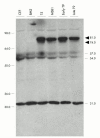
Results: In T9 cells maintained in culture for up to six months (late T9), the MDV ICP4 gene was disrupted, whereas the meq gene was actively transcribed. The alterations of the MDV genome in these cells correlated with the inability of the virus to induce the classic signs of Marek's disease in 1 day old chickens. However, early T9 cells submitted to a limited number of passages induced classic MDV pathogenicity, as efficiently as the MDV control cell line (T5), and did not show gross structural changes in the oncogenic MDV sequences.
Conclusions: Although the expression pattern of the MDV oncogenes in early T9 cells was identical to the one reported for other MDV transformed cells, longterm culture of an MDV transformed cell line containing a RAV insertional activation of the c-myb protooncogene led to the disruption of the MDV BamHI-H and BamHI-A oncogenic regions. In the late T9 cells MEQ was the only detected MDV oncoprotein. These results suggest that in the late T9 cells the truncated MYB protein compensates for the loss of MDV oncoproteins and reinforce the possibility that MEQ and MYB cooperate in the maintenance of the transformed state and the tumorigenic potential of these cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Retroviral insertional activation of the c-myb proto-oncogene in a Marek's disease T-lymphoma cell line.J Virol. 1996 Nov;70(11):7414-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.11.7414-7423.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8892859 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid insertion in the Meq protein of Marek's disease virus, an avian oncogenic herpesvirus, accelerates tumorigenesis.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Aug 5;13(8):e0336824. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03368-24. Epub 2025 Jul 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40673706 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of Marek's disease virus (MDV) cDNAs mapping to the BamHI-I2, BamHI-Q2, and BamHI-L fragments of the MDV genome from lymphoblastoid cells transformed and persistently infected with MDV.Virology. 1995 Nov 10;213(2):590-9. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.0031. Virology. 1995. PMID: 7491783
-
Latency and tumorigenesis in Marek's disease.Avian Dis. 2013 Jun;57(2 Suppl):360-5. doi: 10.1637/10470-121712-Reg.1. Avian Dis. 2013. PMID: 23901747 Review.
-
T-cell transformation by Marek's disease virus.Trends Microbiol. 1999 Jan;7(1):22-9. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(98)01427-9. Trends Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10068994 Review.
References
-
- Ross NL. T-cell transformation by Marek’s disease virus. Trends Microbiol 1999;7:22–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
