Circadian variation in blood pressure: dipper or nondipper
- PMID: 12147922
- PMCID: PMC8101874
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2002.01033.x
Circadian variation in blood pressure: dipper or nondipper
Abstract
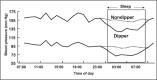
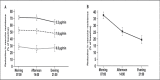
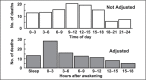
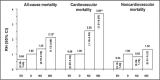
Awareness of an increased incidence of cardiovascular events shortly after awakening has heightened interest in the chronopathology of cardiovascular diseases. Blood pressure varies according to cycles characterized by a reduction during sleep and an increase on awakening. The surge in blood pressure coincides with the circadian nature of various endocrine and hematologic parameters that also have a putative role in triggering the onset of cardiovascular events. The nighttime decrease is absent or blunted in some hypertensive patients (termed nondippers), an effect associated with increased morbidity. Drugs can influence the effect of these circadian patterns. Research efforts are focused on clarifying an underlying pathophysiologic process that could be modified by pharmacologic or other means. Long-acting angiotensin II receptor blockers have an effect on blood pressure over 24 hours due to their long half-life, but could also limit the morning surge in blood pressure through an effect on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone and noradrenergic systems.
Copyright 2002 Le Jacq Communications, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Muller JE, Stone PH, Turi ZG, et al. Circadian variation in the frequency of onset of acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1985;313:1315–1323. - PubMed
-
- Willich SN, Goldberg RJ, Maclure M, et al. Increased onset of sudden cardiac death in the first three hours after awakening. Am J Cardiol. 1992;70:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Neaton JD, Kuller L, Stamler J, et al. Impact of systolic and diastolic blood pressure on cardiovascular mortality. In: Laragh JH, Brenner BM, eds. Hypertension: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Management. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Raven Press; 1995:127–144.
-
- MacMahon S, Peto R, Cutler J, et al. Blood pressure, stroke, and coronary heart disease. Lancet. 1990;335:765–774. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Sega R, Milesi C, et al. Blood‐pressure control in the hypertensive population. Lancet. 1997;349:454–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

