Decreased expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor promotes growth of human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 12149131
- PMCID: PMC117795
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-2-18
Decreased expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor promotes growth of human breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Loss or mutation of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor (M6P/IGF2R) has been found in breast cancer. However, whether or not decreased levels of functional M6P/IGF2R directly contribute to the process of carcinogenesis needs to be further verified by functional studies.
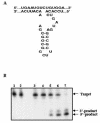
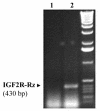
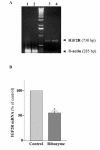
Methods: In this study, using viral and ribozyme strategies we reduced the expression of M6P/IGF2R in human breast cancer cells and then examined the effect on growth and apoptosis of these cells.
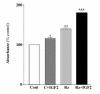
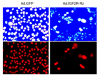
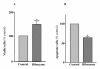
Results: Our results showed that infection of MCF-7 cells with the adenovirus carrying a ribozyme targeted against the M6P/IGF2R mRNA dramatically reduced the level of transcripts and the functional activity of M6P/IGF2R in these cells. Accordingly, cells treated with a ribozyme exhibited a higher growth rate and a lower apoptotic index than control cells (infected with a control vector). Furthermore, decreased expression of M6P/IGF2R enhanced IGF-II-induced proliferation and reduced cell susceptibility to TNF-induced apoptosis.
Conclusions: These results suggest that M6P/IGF2R functions as a growth suppressor and its loss or mutation may contribute to development and progression of cancer. This study also demonstrates that adenoviral delivery of the ribozyme provides a useful tool for investigating the role of M6P/IGF2R in regulation of cell growth.
Figures
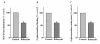
Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of the M6P/IGF-II receptor increases cell proliferation and reduces apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes.BMC Cell Biol. 2004 Apr 28;5:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-5-15. BMC Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15115542 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/ insulin-like growth factor-II receptor in human breast cancer cell lines of different invasive potential.Med Sci Monit. 2002 Aug;8(8):BR293-300. Med Sci Monit. 2002. PMID: 12165733
-
Mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor mediates the growth-inhibitory effects of retinoids.Cell Growth Differ. 1999 Aug;10(8):591-600. Cell Growth Differ. 1999. PMID: 10470859
-
The mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (M6P/IGF2R), a putative breast tumor suppressor gene.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998 Feb;47(3):269-81. doi: 10.1023/a:1005959218524. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998. PMID: 9516081 Review.
-
Mannose-6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (M6P/IGF2R) in carcinogenesis.Cancer Lett. 2010 Mar 1;289(1):11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.06.036. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Cancer Lett. 2010. PMID: 19646808 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor is a key immune-related gene that is correlated with a poor prognosis in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: A bioinformatics analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 18;12:871786. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.871786. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36330486 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of IGF2R evades lysosomal dysfunction-induced apoptosis of cervical cancer cells via transport of cathepsins.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Nov 20;10(12):876. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2117-9. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31748500 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of alpha-interferon on insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor-II and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 secretion by a human lung cancer cell line in vitro.J Endocrinol Invest. 2005 May;28(5):432-9. doi: 10.1007/BF03347224. J Endocrinol Invest. 2005. PMID: 16075927
-
Clinical significance of loss of heterozygosity for M6P/IGF2R in patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar 7;14(9):1394-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1394. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18322954 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Immunotherapy Efficacy with Machine Learning in Gastrointestinal Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 20;26(13):5937. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135937. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649716 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

