Decreased expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor promotes growth of human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 12149131
- PMCID: PMC117795
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-2-18
Decreased expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor promotes growth of human breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Loss or mutation of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor (M6P/IGF2R) has been found in breast cancer. However, whether or not decreased levels of functional M6P/IGF2R directly contribute to the process of carcinogenesis needs to be further verified by functional studies.
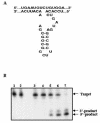
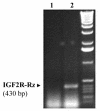
Methods: In this study, using viral and ribozyme strategies we reduced the expression of M6P/IGF2R in human breast cancer cells and then examined the effect on growth and apoptosis of these cells.
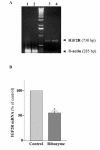
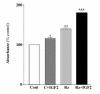
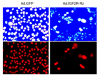
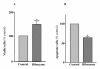
Results: Our results showed that infection of MCF-7 cells with the adenovirus carrying a ribozyme targeted against the M6P/IGF2R mRNA dramatically reduced the level of transcripts and the functional activity of M6P/IGF2R in these cells. Accordingly, cells treated with a ribozyme exhibited a higher growth rate and a lower apoptotic index than control cells (infected with a control vector). Furthermore, decreased expression of M6P/IGF2R enhanced IGF-II-induced proliferation and reduced cell susceptibility to TNF-induced apoptosis.
Conclusions: These results suggest that M6P/IGF2R functions as a growth suppressor and its loss or mutation may contribute to development and progression of cancer. This study also demonstrates that adenoviral delivery of the ribozyme provides a useful tool for investigating the role of M6P/IGF2R in regulation of cell growth.
Figures
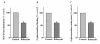
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

