Visualizing the genome: techniques for presenting human genome data and annotations
- PMID: 12149135
- PMCID: PMC119855
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-3-19
Visualizing the genome: techniques for presenting human genome data and annotations
Abstract
Background: In order to take full advantage of the newly available public human genome sequence data and associated annotations, biologists require visualization tools ("genome browsers") that can accommodate the high frequency of alternative splicing in human genes and other complexities.
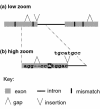
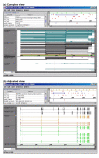
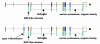
Results: In this article, we describe visualization techniques for presenting human genomic sequence data and annotations in an interactive, graphical format. These techniques include: one-dimensional, semantic zooming to show sequence data alongside gene structures; color-coding exons to indicate frame of translation; adjustable, moveable tiers to permit easier inspection of a genomic scene; and display of protein annotations alongside gene structures to show how alternative splicing impacts protein structure and function. These techniques are illustrated using examples from two genome browser applications: the Neomorphic GeneViewer annotation tool and ProtAnnot, a prototype viewer which shows protein annotations in the context of genomic sequence.
Conclusion: By presenting techniques for visualizing genomic data, we hope to provide interested software developers with a guide to what features are most likely to meet the needs of biologists as they seek to make sense of the rapidly expanding body of public genomic data and annotations.
Figures

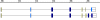
Similar articles
-
Djinn Lite: a tool for customised gene transcript modelling, annotation-data enrichment and exploration.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Jan 23;7:33. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-33. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16426464 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization techniques for genomic data.Proc IEEE Comput Soc Bioinform Conf. 2002;1:321-6. Proc IEEE Comput Soc Bioinform Conf. 2002. PMID: 15838148 Review.
-
GeneViTo: visualizing gene-product functional and structural features in genomic datasets.BMC Bioinformatics. 2003 Oct 31;4:53. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-4-53. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 14594459 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical Viewer: a tool to upload and integrate linkage and association data as plots displayed within the Ensembl genome browser.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Apr 12;6:95. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-95. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15826305 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Exon-Intron Database (EID).Brief Bioinform. 2006 Jun;7(2):178-85. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbl003. Epub 2006 Mar 9. Brief Bioinform. 2006. PMID: 16772261 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome Projector: zoomable genome map with multiple views.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Jan 23;10:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-31. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19166610 Free PMC article.
-
Djinn Lite: a tool for customised gene transcript modelling, annotation-data enrichment and exploration.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Jan 23;7:33. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-33. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16426464 Free PMC article.
-
High-Performance Integrated Virtual Environment (HIVE) Tools and Applications for Big Data Analysis.Genes (Basel). 2014 Sep 30;5(4):957-81. doi: 10.3390/genes5040957. Genes (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25271953 Free PMC article.
-
On the way to building an integrated computational environment for the study of developmental patterns and genetic diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2006;1(1):89-96. doi: 10.2147/nano.2006.1.1.89. Int J Nanomedicine. 2006. PMID: 17722266 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated genome browser: visual analytics platform for genomics.Bioinformatics. 2016 Jul 15;32(14):2089-95. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw069. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27153568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kulp D, Haussler D, Reese MG, Eeckman FH. A generalized hidden Markov model for the recognition of human genes in DNA. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1996;4:134–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

