Control of P2X(2) channel permeability by the cytosolic domain
- PMID: 12149275
- PMCID: PMC2234464
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.20028535
Control of P2X(2) channel permeability by the cytosolic domain
Abstract
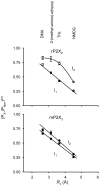
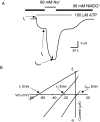
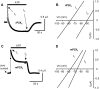
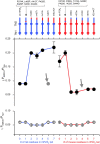
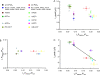
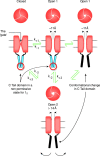
ATP-gated P2X channels are the simplest of the three families of transmitter-gated ion channels. Some P2X channels display a time- and activation-dependent change in permeability as they undergo the transition from the relatively Na(+)-selective I(1) state to the I(2) state, which is also permeable to organic cations. We report that the previously reported permeability change of rat P2X(2) (rP2X(2)) channels does not occur at mouse P2X(2) (mP2X(2)) channels expressed in oocytes. Domain swaps, species chimeras, and point mutations were employed to determine that two specific amino acid residues in the cytosolic tail domain govern this difference in behavior between the two orthologous channels. The change in pore diameter was characterized using reversal potential measurements and excluded field theory for several organic ions; both rP2X(2) and mP2X(2) channels have a pore diameter of approximately 11 A in the I(1) state, but the transition to the I(2) state increases the rP2X(2) diameter by at least 3 A. The I(1) to I(2) transition occurs with a rate constant of approximately 0.5 s(-1). The data focus attention on specific residues of P2X(2) channel cytoplasmic domains as determinants of permeation in a state-specific manner.
Figures
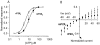


Similar articles
-
Contribution of transmembrane regions to ATP-gated P2X2 channel permeability dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 18;280(7):6118-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411324200. Epub 2004 Nov 19. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15556949
-
Coexpression of rat P2X2 and P2X6 subunits in Xenopus oocytes.J Neurosci. 2000 Jul 1;20(13):4871-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-13-04871.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10864944 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics to identify proteins interacting with P2X2 ligand-gated cation channels.J Vis Exp. 2009 May 18;(27):1178. doi: 10.3791/1178. J Vis Exp. 2009. PMID: 19455095 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysics of P2X receptors.Pflugers Arch. 2006 Aug;452(5):501-12. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0078-1. Epub 2006 May 13. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16708237 Review.
-
Molecular physiology of P2X receptors.Physiol Rev. 2002 Oct;82(4):1013-67. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00015.2002. Physiol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12270951 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular properties of P2X receptors.Pflugers Arch. 2006 Aug;452(5):486-500. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0073-6. Epub 2006 Apr 11. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16607539 Review.
-
Regions of the amino terminus of the P2X receptor required for modification by phorbol ester and mGluR1alpha receptors.J Neurochem. 2009 Jan;108(2):331-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05761.x. Epub 2008 Nov 22. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19046321 Free PMC article.
-
Novel channel-mediated choline transport in cholinergic neurons of the mouse retina.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Oct 1;118(4):1952-1961. doi: 10.1152/jn.00506.2016. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28701543 Free PMC article.
-
Two open states of P2X receptor channels.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Nov 14;7:215. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00215. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24312007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the permeation of large organic cations through the pore of ATP-gated P2X receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 May 9;114(19):E3786-E3795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701379114. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28442564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barry, P.H., and J.W. Lynch. 1991. Liquid junction potentials and small cell effects in ptach-clamp analysis. J. Membrane Biol. 121:101–117. - PubMed
-
- Boue-Grabot, E., V. Archambault, and P. Seguela. 2000. A protein kinase C site highly conserved in P2X subunits controls the desensitization kinetics of P2X(2) ATP-gated channels. J. Biol. Chem. 275:10190–10195. - PubMed
-
- Ding, S., and F. Sachs. 1999. b. Ion permeation and block of P2X2 purinoceptors: single channel recordings. J. Membr. Biol. 172:215–223. - PubMed

