Multiplex PCR assays for simultaneous detection of six major serotypes and two virulence-associated phenotypes of Streptococcus suis in tonsillar specimens from pigs
- PMID: 12149353
- PMCID: PMC120666
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.8.2922-2929.2002
Multiplex PCR assays for simultaneous detection of six major serotypes and two virulence-associated phenotypes of Streptococcus suis in tonsillar specimens from pigs
Abstract
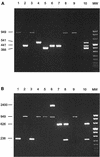
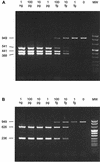
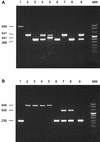
Multiplex PCR assays for the detection and identification of various Streptococcus suis strains in tonsillar specimens from pigs were developed and evaluated. In two separate reactions, five distinct DNA targets were amplified. Three targets, based on the S. suis capsular polysaccharide (cps) genes specific for serotypes 1 (and 14), 7, and 9, were amplified in multiplex PCR I. Two other targets, based on the serotype 2- (and 1/2-) specific cps gene and the epf gene, encoding the EF proteins of virulent serotype 2 and highly virulent serotype 1 strains, were amplified in multiplex PCR II. To identify false-negative results, firefly luciferase (luc) DNA and primers based on the luc gene were included in the assay. The multiplex PCR assays were evaluated with tonsillar specimens from pigs infected with S. suis strains. The results obtained with the PCR assays were compared with the results obtained with a bacteriological examination. Most (94%) of the results obtained with multiplex PCR assays were confirmed by the bacteriological examination. The PCR method seems to be more sensitive compared to the bacteriological method, since the remaining 6% of the samples were positive by PCR and negative by bacteriological examination. These results indicate that the PCR method is highly specific for the detection of S. suis strains most frequently involved in clinical disease in infected pig herds. The serotypes found by PCR in tonsillar specimens from diseased pigs were compared with the serotypes of the strains isolated from the affected tissues of the same pigs. The results showed that there is significant association between carriership and clinical illness for S. suis serotype 9 and EF-positive serotype 2 strains and not for serotype 7 and EF-negative serotype 2 (or 1/2) strains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of virulent strains of Streptococcus suis type 2 and highly virulent strains of Streptococcus suis type 1 in tonsillar specimens of pigs by PCR.Vet Microbiol. 1999 Jun 15;67(2):143-57. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(99)00036-x. Vet Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10414368
-
Development of rapid serotype-specific PCR assays for eight serotypes of Streptococcus suis.J Clin Microbiol. 2012 Oct;50(10):3329-34. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01584-12. Epub 2012 Aug 8. J Clin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22875885 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence-associated gene profiling of Streptococcus suis isolates by PCR.Vet Microbiol. 2006 Jun 15;115(1-3):117-27. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2005.12.013. Epub 2006 Jan 20. Vet Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16431041
-
Detection and molecular typing of Streptococcus suis in tonsils from live pigs in France.Can J Vet Res. 2007 Jan;71(1):14-22. Can J Vet Res. 2007. PMID: 17193877 Free PMC article.
-
Colonization of suckling pigs by Streptococcus suis with particular reference to pathogenic serotype 2 strains.Can J Vet Res. 1998 Jan;62(1):21-6. Can J Vet Res. 1998. PMID: 9442935 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting AI-2 quorum sensing: harnessing natural products against Streptococcus suis biofilm infection.Vet Res. 2025 Feb 4;56(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01450-x. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 39905565 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the population structure of invasive Streptococcus suis strains isolated from pigs and from humans in The Netherlands.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e33854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033854. Epub 2012 May 1. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22563452 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Simultaneous Exposure of Pigs to Streptococcus suis Serotypes 2 and 9 on Their Colonization and Transmission, and on Mortality.Pathogens. 2017 Sep 27;6(4):46. doi: 10.3390/pathogens6040046. Pathogens. 2017. PMID: 28953248 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of MALDI-TOF MS as Alternative Tool for Streptococcus suis Identification.Front Public Health. 2015 Aug 21;3:202. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2015.00202. eCollection 2015. Front Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26347858 Free PMC article.
-
Increased production of suilysin contributes to invasive infection of the Streptococcus suis strain 05ZYH33.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Dec;10(6):2819-26. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2586. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 25241621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allgaier, A., R. Goethe, H. J. Wisselink, H. E. Smith, and P. Valentin Weigand. 2001. Relatedness of Streptococcus suis isolates of various serotypes and clinical backgrounds as evaluated by macrorestriction analysis and expression of potential virulence traits. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:445-453. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chengappa, M. M., L. W. Pace, J. A. Williams, C. H. Herren, and S. E. Ascher. 1990. Efficacy of tiamulin against experimentally induced Streptococcus suis type-2 infection in swine. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 197:1467-1470. - PubMed
-
- Devriese, L. A., K. Ceyssens, J. Hommez, R. Kilpper Balz, and K. H. Schleifer. 1991. Characteristics of different Streptococcus suis ecovars and description of a simplified identification method. Vet. Microbiol. 26:141-150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

