Dealing with osmostress through MAP kinase activation
- PMID: 12151331
- PMCID: PMC1084212
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf158
Dealing with osmostress through MAP kinase activation
Abstract
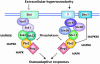
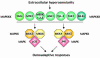
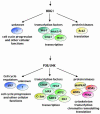
In response to changes in the extracellular environment, cells coordinate intracellular activities to maximize their probability of survival and proliferation. Eukaryotic cells, from yeast to mammals, transduce diverse extracellular stimuli through the cell by multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades. Exposure of cells to increases in extracellular osmolarity results in rapid activation of a highly conserved family of MAPKs, known as stress-activated MAPKs (SAPKs). Activation of SAPKs is essential for the induction of adaptive responses required for cell survival upon osmostress. Recent studies have begun to shed light on the broad effects of SAPK activation in the modulation of several aspects of cell physiology, ranging from the control of gene expression to the regulation of cell division.
Figures

References
-
- Alepuz P.M., Jovanovic, A., Reiser, V. and Ammerer, G. (2001) Stress-induced map kinase Hog1 is part of transcription activation complexes. Mol. Cell, 7, 767–777. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosino C. and Nebreda, A.R. (2001) Cell cycle regulation by p38 MAP kinases. Biol. Cell, 93, 47–51. - PubMed
-
- Carter A.B., Knudtson, K.L., Monick, M.M. and Hunninghake, G.W. (1999) The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for NF-κB-dependent gene expression. The role of TATA-binding protein (TBP). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 30858–30863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

