The Zebrafish motility mutant twitch once reveals new roles for rapsyn in synaptic function
- PMID: 12151528
- PMCID: PMC6758142
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-15-06491.2002
The Zebrafish motility mutant twitch once reveals new roles for rapsyn in synaptic function
Abstract
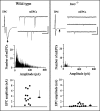
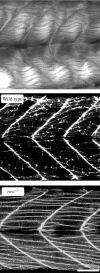
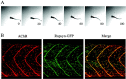
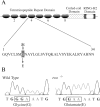
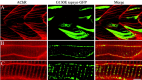
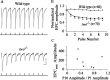
Upon touch, twitch once zebrafish respond with one or two swimming strokes instead of typical full-blown escapes. This use-dependent fatigue is shown to be a consequence of a mutation in the tetratricopeptide domain of muscle rapsyn, inhibiting formation of subsynaptic acetylcholine receptor clusters. Physiological analysis indicates that reduced synaptic strength, attributable to loss of receptors, is augmented by a potent postsynaptic depression not seen at normal neuromuscular junctions. The synergism between these two physiological processes is causal to the use-dependent muscle fatigue. These findings offer insights into the physiological basis of human myasthenic syndrome and reveal the first demonstration of a role for rapsyn in regulating synaptic function.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fatigue in Rapsyn-Deficient Zebrafish Reflects Defective Transmitter Release.J Neurosci. 2016 Oct 19;36(42):10870-10882. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0505-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27798141 Free PMC article.
-
Paralytic zebrafish lacking acetylcholine receptors fail to localize rapsyn clusters to the synapse.J Neurosci. 2001 Aug 1;21(15):5439-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-15-05439.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11466415 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamics of the rapsyn scaffolding protein at individual acetylcholine receptor clusters.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 30;282(13):9932-9940. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608714200. Epub 2007 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17283077
-
Recombinant neuromuscular synapses.Bioessays. 1992 Oct;14(10):671-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141005. Bioessays. 1992. PMID: 1365879 Review.
-
Clustering of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from the neuromuscular junction to interneuronal synapses.Mol Neurobiol. 2002 Feb;25(1):79-112. doi: 10.1385/MN:25:1:079. Mol Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 11890459 Review.
Cited by
-
Zebrafish neuromuscular junction: The power of N.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Nov 20;713:134503. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134503. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 31557523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function of neuromuscular synapses in the zebrafish choline-acetyltransferase mutant bajan.J Neurophysiol. 2008 Oct;100(4):1995-2004. doi: 10.1152/jn.90517.2008. Epub 2008 Aug 6. J Neurophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18684905 Free PMC article.
-
Essential roles of the acetylcholine receptor gamma-subunit in neuromuscular synaptic patterning.Development. 2008 Jun;135(11):1957-67. doi: 10.1242/dev.018119. Epub 2008 Apr 23. Development. 2008. PMID: 18434415 Free PMC article.
-
How do genes regulate simple behaviours? Understanding how different neurons in the vertebrate spinal cord are genetically specified.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2006 Jan 29;361(1465):45-66. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1778. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16553308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The beta-adrenergic agonist salbutamol modulates neuromuscular junction formation in zebrafish models of human myasthenic syndromes.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 May 1;27(9):1556-1564. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy062. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29462491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agius MA, Zhu S, Kirvan CA, Schafer AL, Lin MY, Fairclough RH, Oger JJ, Aziz T, Aarli JA. Rapsyn antibodies in myasthenia gravis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1998;841:516–521. - PubMed
-
- Apel ED, Glass DJ, Moscoso LM, Yancopoulos GD, Sanes JR. Rapsyn is required for MuSK signaling and recruits synaptic components to a MuSK-containing scaffold. Neuron. 1997;18:623–635. - PubMed
-
- Behra M, Cousin X, Bertrand C, Vonesch JL, Biellmann D, Chatonnet A, Strahle U. Acetylcholinesterase is required for neuronal and muscular development in the zebrafish embryo. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:111–118. - PubMed
-
- Burden SJ. The formation of neuromuscular synapses. Genes Dev. 1998;12:133–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
