Ceruloplasmin regulates iron levels in the CNS and prevents free radical injury
- PMID: 12151537
- PMCID: PMC6758125
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-15-06578.2002
Ceruloplasmin regulates iron levels in the CNS and prevents free radical injury
Abstract
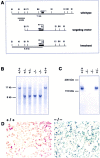
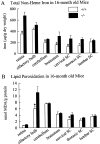
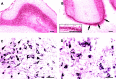
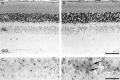
Ceruloplasmin is a ferroxidase that oxidizes toxic ferrous iron to its nontoxic ferric form. We have previously reported that a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored form of ceruloplasmin is expressed in the mammalian CNS. To better understand the role of ceruloplasmin in iron homeostasis in the CNS, we generated a ceruloplasmin gene-deficient (Cp(-/-)) mouse. Adult Cp(-/-) mice showed increased iron deposition in several regions of the CNS such as the cerebellum and brainstem. Increased lipid peroxidation was also seen in some CNS regions. Cerebellar cells from neonatal Cp(-/-) mice were also more susceptible to oxidative stress in vitro. Cp(-/-) mice showed deficits in motor coordination that were associated with a loss of brainstem dopaminergic neurons. These results indicate that ceruloplasmin plays an important role in maintaining iron homeostasis in the CNS and in protecting the CNS from iron-mediated free radical injury. Therefore, the antioxidant effects of ceruloplasmin could have important implications for various neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease in which iron deposition is known to occur.
Figures


References
-
- Andrews NC. The iron transporter DMT1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;31:991–994. - PubMed
-
- Boll M-C, Sotelo J, Otero E, Alcaraz-Zubeldia M, Rios C. Reduced ferroxidase activity in the cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1999;265:155–158. - PubMed
-
- Borg DC, Schaich KM. Prooxidant action of desferrioxamine: Fenton-like production of hydroxyl radicals by reduced ferrioxamine. J Free Radic Biol Med. 1986;2:237–243. - PubMed
-
- Bowie AG, Moynagh PN, O'Neill LAJ. Lipid peroxidation is involved in the activation of NF-kappaB by tumor necrosis factor but not interleukin-1 in the human endothelial cell line ECV304. Lack of involvement of H2O2 in NF-kappaB activation by either cytokine in both primary and transformed endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:25941–25950. - PubMed
-
- Choi SY, Kwon HY, Kwon OB, Eum WS, Kang JH. Fragmentation of human ceruloplasmin induced by hydrogen peroxide. Biochimie. 2000;82:175–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
