Partial peripheral nerve injury promotes a selective loss of GABAergic inhibition in the superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord
- PMID: 12151551
- PMCID: PMC6758148
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-15-06724.2002
Partial peripheral nerve injury promotes a selective loss of GABAergic inhibition in the superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord
Abstract
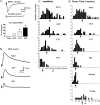
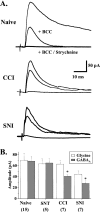
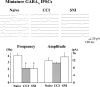
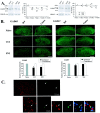
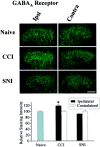
To clarify whether inhibitory transmission in the superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord is reduced after peripheral nerve injury, we have studied synaptic transmission in lamina II neurons of an isolated adult rat spinal cord slice preparation after complete sciatic nerve transection (SNT), chronic constriction injury (CCI), or spared nerve injury (SNI). Fast excitatory transmission remains intact after all three types of nerve injury. In contrast, primary afferent-evoked IPSCs are substantially reduced in incidence, magnitude, and duration after the two partial nerve injuries, CCI and SNI, but not SNT. Pharmacologically isolated GABA(A) receptor-mediated IPSCs are decreased in the two partial nerve injury models compared with naive animals. An analysis of unitary IPSCs suggests that presynaptic GABA release is reduced after CCI and SNI. Partial nerve injury also decreases dorsal horn levels of the GABA synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) 65 kDa ipsilateral to the injury and induces neuronal apoptosis, detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated biotinylated UTP nick end labeling staining in identified neurons. Both of these mechanisms could reduce presynaptic GABA levels and promote a functional loss of GABAergic transmission in the superficial dorsal horn.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez FJ, Taylor-Blake B, Fyffe RE, De Blas AL, Light AR. Distribution of immunoreactivity for the β2 and β3 subunits of the GABAA receptor in the mammalian spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1996;365:392–412. - PubMed
-
- Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988;33:87–107. - PubMed
-
- Bennett GJ, Kajander KC, Saraha Y, Iadarola MJ, Sugimoto T. Neurochemical and anatomical changes in the dorsal horn of rats with an experimental peripheral neuropathy. In: Cervero F, Bennett GJ, Headley PM, editors. Processing of sensory information in the superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Plenum; New York: 1989. pp. 463–471.
-
- Bhisitkul RB, Kocsis JD, Gordon TR, Waxman SG. Trophic influence of the distal nerve segment on GABAA receptor expression in axotomized adult sensory neurons. Exp Neurol. 1990;109:273–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
