The ability of antigen, but not interleukin-2, to promote n-butyrate-induced T helper 1 cell anergy is associated with increased expression and altered association patterns of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 12153511
- PMCID: PMC1782758
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2002.01457.x
The ability of antigen, but not interleukin-2, to promote n-butyrate-induced T helper 1 cell anergy is associated with increased expression and altered association patterns of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
Abstract
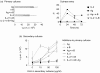
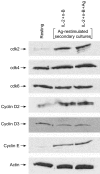
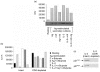
The ability of the cell cycle inhibitor n-butyrate to induce T helper 1 (Th1) cell anergy is dependent upon its ability to block the cell cycle progression of activated Th1 cells in G1. Results reported here show that although both interleukin (IL)-2 and antigen (Ag) push Th1 cells into G1 where they are blocked by n-butyrate, only the Ag-activated Th1 cells demonstrate functional anergy once the n-butyrate has been removed from the culture. Because n-butyrate-induced Th1 cell anergy has been linked to increased expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21Cip1 and p27Kip1, mechanistic experiments focused on the role of these inhibitors. It was found that when Th1 cells were reincubated in Ag-stimulated secondary cultures, the Th1 cells previously exposed to Ag and n-butyrate (anergic Th1 cells) demonstrated a cumulative increase in p21Cip1 and p27Kip1 when compared with Th1 cells previously exposed to recombinant (r)IL-2 and n-butyrate (non-anergic Th1 cells). p27Kip1 in the anergic Th1 cells from the secondary cultures was associated with cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks). In contrast, p21Cip1 in the anergic Th1 cells, although present at high levels, did not associate significantly with cdks, suggesting that p21Cip1 may target some other protein in the anergic Th1 cells. Taken together, these findings suggest that Th1 cell exposure to Ag and n-butyrate, rather than IL-2 and n-butyrate, is needed to induce the cumulative increase in p21Cip1 and p27Kip1 that is associated with the proliferative unresponsiveness in anergic Th1 cells. In addition, p21Cip1 may inhibit proliferation in the anergic Th1 cells by some mechanism other than suppression of cdks that is unique to the induction of Th1 cell anergy.
Figures




Similar articles
-
p21(Cip1) up-regulated during histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced CD4(+) T-cell anergy selectively associates with mitogen-activated protein kinases.Immunology. 2010 Apr;129(4):589-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03161.x. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20102411 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of anergy in Th1 cells associated with increased levels of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21Cip1 and p27Kip1.J Immunol. 2001 Jan 15;166(2):952-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.2.952. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11145672
-
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p27Kip1 and p21Cip1 are not essential in T cell anergy.Eur J Immunol. 2003 Nov;33(11):3154-63. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323960. Eur J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14579284
-
Helper T cell anergy: from biochemistry to cancer pathophysiology and therapeutics.J Mol Med (Berl). 2001;78(12):673-83. doi: 10.1007/s001090000180. J Mol Med (Berl). 2001. PMID: 11434720 Review.
-
[Molecular mechanisms controlling the cell cycle: fundamental aspects and implications for oncology].Cancer Radiother. 2001 Apr;5(2):109-29. doi: 10.1016/s1278-3218(01)00087-7. Cancer Radiother. 2001. PMID: 11355576 Review. French.
Cited by
-
p21(Cip1) up-regulated during histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced CD4(+) T-cell anergy selectively associates with mitogen-activated protein kinases.Immunology. 2010 Apr;129(4):589-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03161.x. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20102411 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC inhibition prevents transgene expression downregulation and loss-of-function in T-cell-receptor-transduced T cells.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021 Jan 26;20:352-363. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.01.014. eCollection 2021 Mar 26. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021. PMID: 33614916 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic short chain fatty acids limit antitumor effect of CTLA-4 blockade in hosts with cancer.Nat Commun. 2020 May 1;11(1):2168. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16079-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32358520 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Gut Microbiome-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acid Butyrate in Hepatobiliary Diseases.Am J Pathol. 2023 Oct;193(10):1455-1467. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.06.007. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Am J Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37422149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinases: molecular switches controlling anergy and potential therapeutic targets for tolerance.Semin Immunol. 2007 Jun;19(3):173-9. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.02.009. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17383195 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Quill H, Schwartz RH. Stimulation of normal inducer T cell clones with antigen presented by purified Ia molecules in planar lipid membranes: specific induction of a long-lived state of proliferative nonresponsiveness. J Immunol. 1987;138:3704. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert KM, Weigle WO. Th1 cell anergy and blockade in G1a phase of the cell cycle. J Immunol. 1993;151:1245–54. - PubMed
-
- Jackson SK, DeLoose A, Gilbert KM. Induction of anergy in Th1 cells associated with increased levels of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21Cip1 and p27Kip1. J Immunol. 2001;166:952–8. - PubMed
-
- Aprelikova O, Xiong Y, Liu ET. Both p16 and p21 families of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors block the phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinases by the CDK-activating kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:18195–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

