Differential chromatin structure within a tandem array 100 kb upstream of the maize b1 locus is associated with paramutation
- PMID: 12154122
- PMCID: PMC186425
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1006702
Differential chromatin structure within a tandem array 100 kb upstream of the maize b1 locus is associated with paramutation
Abstract
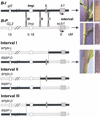
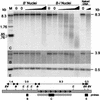
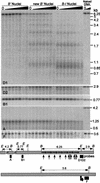
Recombination mapping defined a 6-kb region, 100 kb upstream of the transcription start site, that is required for B-I enhancer activity and paramutation-a stable, heritable change in transcription caused by allele interactions in maize (Zea mays). In this region, B-I and B' (the only b1 alleles that participate in paramutation) have seven tandem repeats of an 853-bp sequence otherwise unique in the genome; other alleles have one. Examination of recombinant alleles with different numbers of tandem repeats indicates that the repeats are required for both paramutation and enhancer function. The 6-kb region is identical in B-I and B', showing that epigenetic mechanisms mediate the stable silencing associated with paramutation. This is the first endogenous gene for which sequences required for paramutation have been defined and examined for methylation and chromatin structure. The tandem repeat sequences are more methylated in B-I (high expressing) relative to B' (low expressing), opposite of the typical correlation. Furthermore, the change in repeat methylation follows establishment of the B' epigenetic state. B-I has a more open chromatin structure in the repeats relative to B'. The nuclease hypersensitivity differences developmentally precede transcription, suggesting that the repeat chromatin structure could be the heritable imprint distinguishing the two transcription states.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The role of DNA methylation, nucleosome occupancy and histone modifications in paramutation.Plant J. 2010 Aug;63(3):366-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04245.x. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 20444233
-
The regulatory regions required for B' paramutation and expression are located far upstream of the maize b1 transcribed sequences.Genetics. 2002 Oct;162(2):917-30. doi: 10.1093/genetics/162.2.917. Genetics. 2002. PMID: 12399399 Free PMC article.
-
Sequences required for paramutation of the maize b gene map to a region containing the promoter and upstream sequences.Genetics. 1995 Aug;140(4):1389-406. doi: 10.1093/genetics/140.4.1389. Genetics. 1995. PMID: 7498778 Free PMC article.
-
Paramutation in maize.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Jun;43(2-3):121-45. doi: 10.1023/a:1006499808317. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10999400 Review.
-
Trans-Homolog Interactions Facilitating Paramutation in Maize.Plant Physiol. 2015 Aug;168(4):1226-36. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00591. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26149572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polyploidy-associated paramutation in Arabidopsis is determined by small RNAs, temperature, and allele structure.PLoS Genet. 2021 Mar 9;17(3):e1009444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009444. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33690630 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics and its implications for plant biology. 1. The epigenetic network in plants.Ann Bot. 2005 Dec;96(7):1143-64. doi: 10.1093/aob/mci273. Epub 2005 Oct 27. Ann Bot. 2005. PMID: 16254022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered nucleosome positions in maize haplotypes and mutants of a subset of SWI/SNF-like proteins.Plant Direct. 2017 Oct 16;1(4):e00019. doi: 10.1002/pld3.19. eCollection 2017 Oct. Plant Direct. 2017. PMID: 31245667 Free PMC article.
-
A Mutator transposon insertion is associated with ectopic expression of a tandemly repeated multicopy Myb gene pericarp color1 of maize.Genetics. 2008 Apr;178(4):1859-74. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.082503. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18430921 Free PMC article.
-
A transgenic, visual screenable marker for soybean seeds.Transgenic Res. 2016 Apr;25(2):187-93. doi: 10.1007/s11248-015-9922-4. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Transgenic Res. 2016. PMID: 26660729
References
-
- Barlow DP. Gametic imprinting in mammals. Science. 1995;270:1610–1613. - PubMed
-
- Bell AC, Felsenfeld G. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature. 2000;405:482–485. - PubMed
-
- Bell AC, West AG, Felsenfeld G. Insulators and boundaries: Versatile regulatory elements in the eukaryotic genome. Science. 2001;291:447–449. - PubMed
-
- Boumil RM, Lee JT. Forty years of decoding the silence in X-chromosome inactivation. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:2225–2232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
