Addition of a photocrosslinking amino acid to the genetic code of Escherichiacoli
- PMID: 12154230
- PMCID: PMC123203
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.172226299
Addition of a photocrosslinking amino acid to the genetic code of Escherichiacoli
Abstract
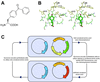
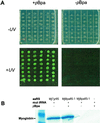
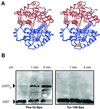
Benzophenones are among the most useful photocrosslinking agents in biology. We have evolved an orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNA pair that makes possible the in vivo incorporation of p-benzoyl-l-phenylalanine into proteins in Escherichia coli in response to the amber codon, TAG. This unnatural amino acid was incorporated with high translational efficiency and fidelity into the dimeric protein glutathione S-transferase. Irradiation resulted in efficient crosslinking (>50%) of the protein subunits. This methodology may prove useful for discovering and defining protein interactions in vitro and in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Wang L., Brock, A., Herberich, B. & Schultz, P. G. (2001) Science 292, 498-500. - PubMed
-
- Dorman G. & Prestwich, G. D. (1994) Biochemistry 33, 5661-5673. - PubMed
-
- Galardy R. E., Craig, L. C. & Printz, M. P. (1973) Nat. New Biol. 242, 127-128. - PubMed
-
- Turro N. J., (1978) Modern Molecular Photochemistry (Benjamin/Cummings Publishing, Menlo Park, CA).
-
- Kauer J. C., Erickson-Viitanen, S., Wolfe, H. R. & DeGrado, W. F. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261, 10695-10700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

