Restriction of lentivirus in monkeys
- PMID: 12154231
- PMCID: PMC129369
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.172384599
Restriction of lentivirus in monkeys
Abstract
Retroviruses are able to cross species barriers and have done so many times throughout evolution. Perhaps as a consequence, dominant mechanisms have arisen to block infection by murine retroviruses in mice (restriction factor Fv1) and humans (restriction factor Ref1), as well as in other mammals. Here we describe a block to HIV and simian immunodeficiency virus in monkeys. Like previously described restrictions the block is saturable and gives rise to multiple-hit infection kinetics. Furthermore, like restriction of murine leukemia virus in humans, the block is before reverse transcription. Intriguingly, African green monkey cells are able to block both HIV and simian immunodeficiency virus, and each virus is able to saturate and abrogate the restriction of the other, suggesting that a common factor is responsible.
Figures
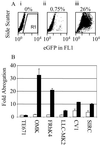
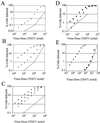
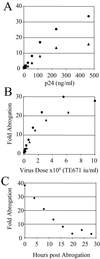
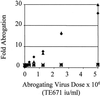
Comment in
-
An intracellular block to primate lentivirus replication.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Sep 3;99(18):11549-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.192449399. Epub 2002 Aug 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12195025 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gao F, Bailes E, Robertson D L, Chen Y, Rodenburg C, Michael S F, Cummins L B, Arthur L O, Peeters M, Shaw G M, Hahn B H. Nature (London) 1999;397:436–441. - PubMed
-
- Weiss R A, Wrangham R W. Nature (London) 1999;397:385–386. - PubMed
-
- Shibata R, Sakai H, Kawamura M, Tokunaga K, Adachi A. J Gen Virol. 1995;76:2723–2730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

