Evidence for a GABA(B) receptor component in the spinal action of Substance P (SP) on arterial blood pressure in the awake rat
- PMID: 12163350
- PMCID: PMC1573441
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704813
Evidence for a GABA(B) receptor component in the spinal action of Substance P (SP) on arterial blood pressure in the awake rat
Abstract
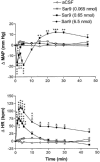
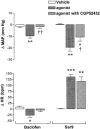
1 The activation of tachykinin NK(1) receptors in the rat spinal cord produced a transient drop in arterial blood pressure followed by a more prolonged pressor effect which is mediated by the stimulation of the sympatho-adrenal system. This study aims at characterizing the spinal mechanism of that initial hypotension occurring in awake unrestrained rats. 2 The initial hypotension (-18+/-2.0 mmHg at 1 min) and the tachycardia (110+/-10 b.p.m.) produced by the intrathecal (i.t.) injection of the stable NK(1) receptor agonist [Sar(9), Met(O(2))(11)]-SP (Sar9, 0.65 nmol) at T-9 spinal cord level was inhibited by the prior injection of 65 nmol LY306740 or LY303870 (NK(1) receptor antagonists). No inhibition was seen when a similar dose of antagonists was given intravenously. 3 The prior i.t. injection of the GABA(B) receptor antagonist CGP52432 (100 nmol) reduced the hypotension evoked by Sar9 (0.65 nmol) and by the GABA(B) receptor agonist baclofen (100 nmol). The GABA(A) receptor antagonist bicuculline (25 nmol, i.t.) was without effect against Sar9, and the GABA(A) agonist muscimol (100 nmol, i.t.) had no cardiovascular effect. 4 The putative involvement of other mediators (dopamine, serotonine, glycine and glutamate) in Sar9-induced hypotension was made unlikely on the basis of various pharmacological treatments. Thus data, suggest that the transient hypotension which occurs upon the activation of NK(1) receptors in the spinal cord is due to the release of GABA which in turn activates GABA(B) receptors to inhibit sympathetic pre-ganglionic fibres. This mechanism may have a physiological significance in the spinal reflex autonomic control of arterial blood pressure.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of cardiovascular sympathetic neurons by substance P and gamma-aminobutyric acid in the rat spinal cord.Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 4;202(1):51-60. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90252-l. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991. PMID: 1723952
-
GABA(A) receptor facilitation of neurokinin release from primary afferent terminals in the rat spinal cord.Neuroscience. 2005;130(4):1013-27. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.10.019. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 15652997
-
Cardiovascular effects of spinal cord substance P: studies with a stable receptor agonist.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jun;233(3):755-60. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985. PMID: 2409270
-
A GABA(B) mystery: the search for pharmacologically distinct GABA(B) receptors.Mol Interv. 2001 Oct;1(4):208-18. Mol Interv. 2001. PMID: 14993343 Review.
-
Bulbospinal substance P and sympathetic regulation of the cardiovascular system: a review.Peptides. 1985;6 Suppl 2:69-74. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90137-8. Peptides. 1985. PMID: 2417209 Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of tachykinin NK-1 and NK-3 receptor binding sites in the spinal cord of spontaneously hypertensive rat: impact on the autonomic control of blood pressure.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 May;148(1):25-38. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706694. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16491095 Free PMC article.
-
Auricular Acupuncture to Lower Blood Pressure Involves the Adrenal Gland in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Nov 20;2020:3720184. doi: 10.1155/2020/3720184. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33273952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BACKMAN S.B., HENRY J.L. Effects of GABA and glycine on sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the upper thoracic intermediolateral nucleus of the cat. Brain Res. 1983;277:365–369. - PubMed
-
- BACKMAN S.B., HENRY J.L. Effects of substance P and thyrotropin-releasing hormone on sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the upper thoracic intermediolateral nucleus of the cat. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1984;62:248–251. - PubMed
-
- BACON S.J., SMITH A.D. Preganglionic sympathetic neurons innervating the rat adrenal medulla: immunocytochemical evidence of synaptic input from nerve terminals containing substance P, GABA or 5-hydroxytryptamine. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1988;24:97–122. - PubMed
-
- BETTLER B., KAUPMANN K., BOWERY N. GABAB receptors: drugs meet clones. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1998;8:345–350. - PubMed
-
- BOGAN N., MENNONE A., CABOT J.B. Light microscopic and ultrastructural localization of GABA-like immunoreactive input to retrogradely labeled sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Brain Res. 1989;505:257–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

