Mechanisms of inhibition of nuclear hormone receptor-dependent hepatitis B virus replication by hepatocyte nuclear factor 3beta
- PMID: 12163577
- PMCID: PMC136416
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.17.8572-8581.2002
Mechanisms of inhibition of nuclear hormone receptor-dependent hepatitis B virus replication by hepatocyte nuclear factor 3beta
Abstract
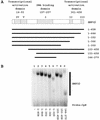
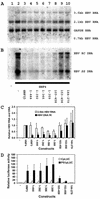
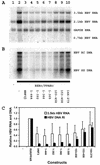
The nuclear hormone receptors hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 (HNF4) and the retinoid X alpha (RXRalpha) plus the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) heterodimer support hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication in nonhepatoma cells. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 (HNF3) inhibits nuclear hormone receptor-mediated viral replication. Inhibition of HBV replication by HNF3beta is associated with the preferential reduction in the level of the pregenomic RNA compared with that of precore RNA. Hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg), encoded by the precore RNA, mediates part of the inhibition of viral replication by HNF3beta. The amino-terminal transcriptional activation domain of HNF3beta is essential for the inhibition of HBV replication. The activation of transcription by HNF3 from HBV promoters downstream from the nucleocapsid promoter appears to contribute indirectly to the reduction in the steady-state level of 3.5-kb HBV RNA, possibly by interfering with the elongation rate of these transcripts. Therefore, transcriptional interference mediated by HNF3 may also regulate HBV RNA synthesis and viral replication.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transcription and replication of a natural hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid promoter variant is regulated in vivo by peroxisome proliferators.Virology. 2001 Oct 25;289(2):239-51. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1169. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11689047
-
Differential regulation of the pre-C and pregenomic promoters of human hepatitis B virus by members of the nuclear receptor superfamily.J Virol. 1997 Dec;71(12):9366-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.12.9366-9374.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9371596 Free PMC article.
-
Avian and Mammalian hepadnaviruses have distinct transcription factor requirements for viral replication.J Virol. 2002 Aug;76(15):7468-72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.15.7468-7472.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12097559 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of hepatitis B virus by nuclear hormone receptors is a critical determinant of viral tropism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 13;98(4):1841-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.4.1841. Epub 2001 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11172038 Free PMC article.
-
Differential inhibition of nuclear hormone receptor-dependent hepatitis B virus replication by the small heterodimer partner.J Virol. 2008 Apr;82(8):3814-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02507-07. Epub 2008 Jan 30. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18234786 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication by hepatocyte nuclear factor 6.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4345-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03094-14. Epub 2015 Feb 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25653429 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic deficiency of the pioneer transcription factor FoxA restricts hepatitis B virus biosynthesis by the developmental regulation of viral DNA methylation.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Feb 24;13(2):e1006239. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006239. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28235042 Free PMC article.
-
Relative DNA Methylation and Demethylation Efficiencies during Postnatal Liver Development Regulate Hepatitis B Virus Biosynthesis.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02148-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02148-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33361417 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the expression levels of Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha and 3 beta in patients with different outcome of HBV infection.Virol J. 2012 Jan 18;9:23. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-23. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22257755 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Dependent Antiviral Activity of Activated cdc42-Associated Kinase 1 Against Hepatitis B Virus.Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 23;12:800935. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.800935. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 35003030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akahane, Y., T. Yamanaka, H. Suzuki, Y. Sugai, F. Tsuda, S. Yotsumoto, S. Omi, H. Okamoto, Y. Miyakawa, and M. Mayumi. 1990. Chronic active hepatitis with hepatitis B virus DNA and antibody against e antigen in the serum. Disturbed synthesis and secretion of e antigen from hepatocytes due to a point mutation in the precore region. Gastroenterology 99:1113-1119. - PubMed
-
- Boshart, M., F. Weber, G. Jahn, K. Dorsch-Hasler, B. Fleckenstein, and W. Schaffner. 1985. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell 41:521-530. - PubMed
-
- Buckwold, V. E., M. Chen, and J. H. Ou. 1997. Interaction of transcription factors RFX1 and MIBP1 with the gamma motif of the negative regulatory element of the hepatitis B virus core promoter. Virology 227:515-518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

