Improvement of endothelial function by amlodipine and vitamin C in essential hypertension
- PMID: 12164090
- PMCID: PMC4531666
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2002.17.2.131
Improvement of endothelial function by amlodipine and vitamin C in essential hypertension
Abstract
Background: The effects of antihypertensive agents on endothelial function have not been fully evaluated in human hypertension and data on the forearm circulation of humans are controversial. The aim of this study was (1) to evaluate the endothelial function in hypertensive patients (2) to investigate whether vitamin C administration has any benefit on the endothelial function and (3) to determine whether treatment with calcium antagonist improves endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive patients.
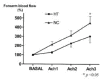
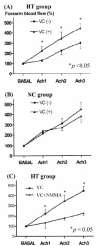
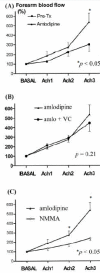
Methods: The endothelial function was estimated using venous occlusion plethysmography (VOP) in 8 hypertensive patients and 8 healthy volunteers. The patients in the hypertension group were treated with amlodipine, then examined again. The change of forearm blood flow (FBF) was measured with acetylcholine infusion through brachial artery and also with intra-arterial vitamin C.
Results: Forearm blood flow response to acetylcholine was significantly enhanced with intra-arterial infusion of vitamin C in hypertensive group before antihypertensive treatment. Co-infusion of L-NMMA, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, blunted forearm blood flow response to acetylcholine. After treatment with amlodipine for 2 months in hypertensive group, endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation to acetylcholine was significantly improved compared to pretreatment, and vitamin C did not affect the improved endothelial function by amlodipine treatment.
Conclusion: Vitamin C (acutely) and amlodipine (chronically) improved endothelial function in hypertensive patients. These results suggest that increased oxidative stress, at least in part, may be involved in the decreased endothelial function in hypertension.
Figures

References
-
- Linder L, Kiowski W, Buhler FR, Luscher TF. Indirect evidence for release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in human forearm circulation in vivo: blunted response in essential hypertension. Circulation. 1990;81:1762–1767. - PubMed
-
- Panza JA, Quyyumi AA, Brush JE, Jr, Epstein SE. Abnormal endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:22–27. - PubMed
-
- Taddei S, Virdis A, Ghiadoni L, Magagna A, Salvetti A. Vitamin C improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation by restoring nitric oxide activity in essential hypertension. Circulation. 1998;97:2222–2229. - PubMed
-
- Egashira K, Suzuki S, Hirooka Y, Kai H, Sugimachi M, Imaizumi T, Takeshita A. Impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation in large epicardial and resistance coronary arteries in patients with essential hypertension: different responses to acetylcholine and substance P. Hypertension. 1995;25:201–206. - PubMed
-
- Higashi Y, Oshima T, Sasaki N, Ishioka N, Nakano Y, Ozono R, Yoshimura M, Ishibashi K, Matsuwa H, Kajiyama G. Relationship between insulin resistance and endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1997;29:280–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
