Metallothionein suppresses collagen-induced arthritis via induction of TGF-beta and down-regulation of proinflammatory mediators
- PMID: 12165078
- PMCID: PMC1906452
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01922.x
Metallothionein suppresses collagen-induced arthritis via induction of TGF-beta and down-regulation of proinflammatory mediators
Abstract
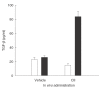
Metallothionein is a low molecular weight, cysteine-rich, stress response protein that can act as an antioxidant and as an immunosuppressive agent in instances of antigen-dependent adaptive immunity. In this context, we assessed the therapeutic potential and mechanisms of action of metallothionein in a collagen-induced arthritis model. Repeated administration of metallothionein-I + II during the course of disease dramatically reduced the incidence and severity of the disease. Joint tissues isolated from boostered paws of metallothionein-I + II-treated mice expressed significantly reduced levels of proinflammatory mediators, such as tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and cyclooxygenase-2, when compared with those of control-treated mice. Lymph node cells obtained from metallothionein-I + II -injected mice exhibited a significant decrease in the proliferative response and a remarkable increase in tumour growth factor (TGF)-beta production in response to type II collagen. Taken together, these results suggest that metallothionein-I + II promote the development of type II collagen-specific, TGF-beta-producing cells to antagonize the expansion of arthritogenic cells. This could lead to local suppression of inflammatory responses by inhibiting the expression of proinflammatory molecules. Thus, this study demonstrates the suppressive effects of metallothionein on collagen-induced arthritis, and indicates that there may be a potential therapeutic application for manipulation of metallothionein during the treatment of autoimmune disorders.
Figures
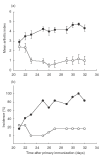

 moderate; ▪ severe.
moderate; ▪ severe.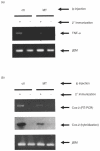

Similar articles
-
Functions of metallothionein generating interleukin-10-producing regulatory CD4+ T cells potentiate suppression of collagen-induced arthritis.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Feb;17(2):348-58. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 18051768
-
Remission of collagen-induced arthritis is associated with high levels of transforming growth factor-beta expression in the joint.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Nov;146(2):287-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03204.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17034581 Free PMC article.
-
Schistosoma mansoni infection reduces severity of collagen-induced arthritis via down-regulation of pro-inflammatory mediators.Int J Parasitol. 2009 Mar;39(4):457-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2008.08.007. Epub 2008 Sep 19. Int J Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 18835272
-
Induction of IL-10-producing CD4+CD25+ T cells in animal model of collagen-induced arthritis by oral administration of type II collagen.Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(3):R213-9. doi: 10.1186/ar1169. Epub 2004 Mar 11. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004. PMID: 15142267 Free PMC article.
-
Metallothioneins: potential therapeutic aids for wound healing in the skin.Wound Repair Regen. 2002 May-Jun;10(3):130-32. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-475x.2002.20101.x. Wound Repair Regen. 2002. PMID: 12164164 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of macrophage CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis in collagen-induced arthritic mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045378. Epub 2012 Sep 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028973 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc and Cadmium in the Aetiology and Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 26;13(1):53. doi: 10.3390/nu13010053. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33375344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metallothionein 1: A New Spotlight on Inflammatory Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 5;12:739918. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.739918. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34804020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type II collagen and gelatin from silvertip shark (Carcharhinus albimarginatus) cartilage: isolation, purification, physicochemical and antioxidant properties.Mar Drugs. 2014 Jun 27;12(7):3852-73. doi: 10.3390/md12073852. Mar Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24979271 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular metallothionein: An alarmin regulating lymphocyte gene expression, cell signaling, and immune function.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2025 Jul 31;30(5):100106. doi: 10.1016/j.cstres.2025.100106. Online ahead of print. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2025. PMID: 40752583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamer DH. Metallothionein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:913–51. - PubMed
-
- Sato M, Bremner I. Oxygen-free radicals and metallothionein. Free Radic Biol Med. 1993;14:325–37. - PubMed
-
- Coyle P, Philcox JC, Rofe AM. Metallothionein induction in cultured rat hepatocytes by arthritic rat serum, activated macrophages, interleukin-6, interleukin-1 and leukaemia inhibitory factor. Inflamm Res. 1995;44:475–81. - PubMed
-
- Basu A, Lazo JS. A hypothesis regarding the protective role of metallothionein against the toxicity of DNA interactive anticancer drug. Toxicol Lett. 1990;50:123–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

