Profiles of cell-to-cell interaction of Mycobacterium intracellulare-induced immunosuppressive macrophages with target T cells in terms of suppressor signal transmission
- PMID: 12165083
- PMCID: PMC1906442
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01890.x
Profiles of cell-to-cell interaction of Mycobacterium intracellulare-induced immunosuppressive macrophages with target T cells in terms of suppressor signal transmission
Abstract
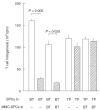
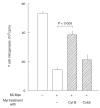
Previously, we have found that immunosuppressive macrophages (M(phi)s) induced by Mycobacterium intracellulare-infection (MI-M(phi)s) required cell contact with target T cells to express their suppressor activity against concanavalin A (Con A)-induced T cell mitogenesis. In this study, we examined the profiles of cell-to-cell interaction of MI-M(phi)s with target T cells. First, MI-M(phi)s displayed suppressor activity in an H-2 allele-unrestricted manner, indicating that MHC molecules are not required for cell contact. The suppressor activity of MI-M(phi)s was reduced markedly by paraformaldehyde fixation or treatment with cytochalasin B or colchicine, indicating that vital membrane functions are required for their suppressor activity. Secondly, the suppressor activity of MI-M(phi)s was independent of cell-to-cell interaction via CD40 ligand/CD40 and M(phi)-derived indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, which causes rapid degradation of tryptophan in T cells. Thirdly, precultivation of splenocytes with MI-M(phi)s, allowing cell-to-cell contact, reduced Con A- or anti-CD3 antibody-induced mitogenesis but not phorbol myristate acetate/calcium ionophore A23187-elicited proliferation of T cells. In addition, co-cultivation of T cells with MI-M(phi)s caused marked changes in profiles of the tyrosine phosphorylation of 33 kDa, 34 kDa and 35-kDa proteins and, moreover, the activation of protein kinase C and its translocation to the cell membrane. It thus appears that suppressor signals of MI-M(phi)s, which are transmitted to the target T cells via cell contact, principally cross-talk with the early signalling events before the activation of PKC and/or intracellular calcium mobilization.
Figures




References
-
- Ellner JJ. Suppressor adherent cells in human tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1978;121:2573–9. - PubMed
-
- Edwards CK, Hedegaar HB, Zlotnik A, et al. Chronic infection due to Mycobacterium intracellulare in mice: association with macrophage release of prostaglandin E2 and reversal by injection of indomethacin, muramyl dipeptide, and interferon-γ. J Immunol. 1986;136:1820–7. - PubMed
-
- Tomioka H. Immunosuppressive macrophages. Clin Immunol. 2000;33:29–36.
-
- Tomioka H, Saito H, Yamada Y. Characteristics of immunosuppressive macrophages induced in spleen cells by Mycobacterium avium complex infections in mice. J Gen Microbiol. 1990;136:965–74. - PubMed
-
- Tomioka H, Saito H, Sato K. Characteristics of immunosuppressive macrophages induced in host spleen cells by Mycobacterium avium complex and Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections in mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1990;34:283–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

