Inactivation of NF-kappaB-dependent cell survival, a novel mechanism for the proapoptotic function of c-Abl
- PMID: 12167702
- PMCID: PMC134000
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.17.6079-6088.2002
Inactivation of NF-kappaB-dependent cell survival, a novel mechanism for the proapoptotic function of c-Abl
Abstract
Using a system that expresses a constitutively kinase-active c-Abl protein [c-Abl(KA)], we identified the protein IkappaBalpha as a novel substrate of c-Abl. This kinase-substrate relationship is not only confirmed at the level of endogenous proteins but is also supported by a physical interaction between the two proteins. Interestingly, the association of c-Abl with IkappaBalpha, which is detectable in the form of nonphosphorylated proteins, is remarkably enhanced by an inducible binding of tyrosine-phosphorylated IkappaBalpha to the c-Abl SH2 domain. In contrast to the serine 32/34 phosphorylation that triggers ubiquitination and degradation of IkappaBalpha, c-Abl-mediated phosphorylation at tyrosine 305 is associated with an increase of the IkappaBalpha protein stability. Significantly, this activity is not shared by the oncogenic Bcr-Abl, because it is unique to the nuclear c-Abl. We also demonstrate that c-Abl targets the nuclear subpopulation of IkappaBalpha for phosphorylation and induces it to accumulate in the nucleus. As a consequence, NF-kappaB transcription activity is abolished, leading to an increased cellular sensitivity to the induction of apoptosis. The functional importance of c-Abl-mediated IkappaBalpha phosphorylation is highlighted by a loss of response of the IkappaBalpha(Y305F) protein to c-Abl-mediated regulation. Using cells expressing the c-Abl(KA) protein under the control of an inducible promoter, we demonstrate inactivation of the NF-kappaB-dependent cell survival pathway as one of the mechanisms for c-Abl-mediated apoptosis.
Figures
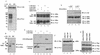





References
-
- Aradhya, S., and D. L. Nelson. 2000. NF-κB signaling and human disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11:300-306. - PubMed
-
- Costanzo, A., P. Merlo, N. Pediconi, M. Fulco, V. Sartorelli, P. A. Cole, G. Fontemaggi, M. Fanciulli, L. Schiltz, G. Blandino, C. Balsano, and M. Levrero. 2002. DNA damage-dependent acetylation of p73 dictates the selective activation of apoptotic target genes. Mol. Cell 9:175-186. - PubMed
-
- Huxford, T., S. Malek, and G. Ghosh. 1999. Structure and mechanism in NF-kappa B/I kappa B signaling. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 64: 533-540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
