Regulation of Wnt/LRP signaling by distinct domains of Dickkopf proteins
- PMID: 12167704
- PMCID: PMC133995
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.17.6100-6110.2002
Regulation of Wnt/LRP signaling by distinct domains of Dickkopf proteins
Abstract
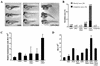
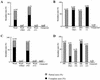
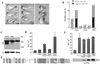
Dickkopfs (Dkks) are secreted developmental regulators composed of two cysteine-rich domains. We report that the effects of Dkks depend on molecular context. Although Wnt8 signaling is inhibited by both Dkk1 and Dkk2 in Xenopus embryos, the same pathway is activated upon interaction of Dkk2 with the Wnt coreceptor LRP6. Analysis of individual Dkk domains and chimeric Dkks shows that the carboxy-terminal domains of both Dkks associate with LRP6 and are necessary and sufficient for Wnt8 inhibition, whereas the amino-terminal domain of Dkk1 plays an inhibitory role in Dkk-LRP interactions. Our study illustrates how an inhibitor of a pathway may be converted into an activator and is the first study to suggest a molecular mechanism for how a ligand other than Wnt can positively regulate beta-catenin signaling.
Figures


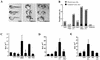
References
-
- Aravind, L., and E. V. Koonin. 1998. A colipase fold in the carboxy-terminal domain of the Wnt antagonists—the Dickkopfs. Curr. Biol. 8:477-478. - PubMed
-
- Bafico, A., G. Liu, A. Yaniv, A. Gazit, and S. A. Aaronson. 2001. Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow. Nat. Cell Biol. 3:683-686. - PubMed
-
- Bhanot, P., M. Brink, C. H. Samos, J. C. Hsieh, Y. Wang, J. P. Macke, D. Andrew, J. Nathans, and R. Nusse. 1996. A new member of the frizzled family from Drosophila functions as a Wingless receptor. Nature 382:225-230. - PubMed
-
- Bouwmeester, T., S. Kim, Y. Sasai, B. Lu, and E. M. De Robertis. 1996. Cerberus is a head-inducing secreted factor expressed in the anterior endoderm of Spemann's organizer. Nature 382:595-601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
