The C.elegans MAPK phosphatase LIP-1 is required for the G(2)/M meiotic arrest of developing oocytes
- PMID: 12169634
- PMCID: PMC126168
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf430
The C.elegans MAPK phosphatase LIP-1 is required for the G(2)/M meiotic arrest of developing oocytes
Abstract
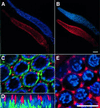
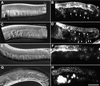
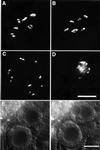
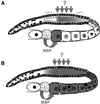
In the Caenorhabditis elegans hermaphrodite germline, spatially restricted mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling controls the meiotic cell cycle. First, the MAPK signal is necessary for the germ cells to progress through pachytene of meiotic prophase I. As the germ cells exit pachytene and enter diplotene/diakinesis, MAPK is inactivated and the developing oocytes arrest in diakinesis (G(2)/M arrest). During oocyte maturation, a signal from the sperm reactivates MAPK to promote M phase entry. Here, we show that the MAPK phosphatase LIP-1 dephosphorylates MAPK as germ cells exit pachytene in order to maintain MAPK in an inactive state during oocyte development. Germ cells lacking LIP-1 fail to arrest the cell cycle at the G(2)/M boundary, and they enter a mitotic cell cycle without fertilization. LIP-1 thus coordinates oocyte cell cycle progression and maturation with ovulation and fertilization.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The adaptor-like protein ROG-1 is required for activation of the Ras-MAP kinase pathway and meiotic cell cycle progression in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genes Cells. 2007 Mar;12(3):407-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2007.01061.x. Genes Cells. 2007. PMID: 17352744
-
Control of oocyte meiotic maturation and fertilization.WormBook. 2005 Dec 28:1-12. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.53.1. WormBook. 2005. PMID: 18050412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Eph receptor sperm-sensing control mechanism for oocyte meiotic maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genes Dev. 2003 Jan 15;17(2):187-200. doi: 10.1101/gad.1028303. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12533508 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK inactivation is required for the G2 to M-phase transition of the first mitotic cell cycle.EMBO J. 1997 Nov 3;16(21):6407-13. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.21.6407. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9351823 Free PMC article.
-
Control of oocyte growth and meiotic maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;757:277-320. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4015-4_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 22872481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-35 buffers apoptosis thresholds in the C. elegans germline by antagonizing both MAPK and core apoptosis pathways.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Dec;26(12):2637-2651. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0325-6. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30952991 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome synthesis and MAPK activity modulate ionizing radiation-induced germ cell apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2013 Nov;9(11):e1003943. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003943. Epub 2013 Nov 21. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24278030 Free PMC article.
-
Reevaluation of the role of LIP-1 as an ERK/MPK-1 dual specificity phosphatase in the C. elegans germline.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jan 18;119(3):e2113649119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2113649119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35022236 Free PMC article.
-
Emergent stem cell homeostasis in the C. elegans germline is revealed by hybrid modeling.Biophys J. 2015 Jul 21;109(2):428-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.007. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26200879 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing Notch signaling antagonizes PRC2-mediated silencing to promote reprograming of germ cells into neurons.Elife. 2016 Sep 7;5:e15477. doi: 10.7554/eLife.15477. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27602485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrieu A., Doree,M. and Fisher,D. (2001) The interplay between cyclin-B–Cdc2 kinase (MPF) and MAP kinase during maturation of oocytes. J. Cell Sci., 114, 257–267. - PubMed
-
- Alessi D.R., Smythe,C. and Keyse,S.M. (1993) The human CL100 gene encodes a Tyr/Thr-protein phosphatase which potently and specifically inactivates MAP kinase and suppresses its activation by oncogenic ras in Xenopus oocyte extracts. Oncogene, 8, 2015–2020. - PubMed
-
- Beitel G.J., Clark,S.G. and Horvitz,H.R. (1990) Caenorhabditis elegans ras gene let-60 acts as a switch in the pathway of vulval induction. Nature, 348, 503–509. - PubMed
-
- Berset T., Hoier,E.F., Battu,G., Canevascini,S. and Hajnal,A. (2001) Notch inhibition of RAS signaling through MAP kinase phosphatase LIP-1 during C.elegans vulval development. Science, 291, 1055–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

